Determine the quadrant in which the angle lies.
?
253°33'
?
A. Quadrant I
B. Quadrant II and Quadrant I
C. Quadrant IV
D. Quadrant III
E. Quadrant II
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Find T, N, and B for the given space curve.r(t) = (ln(cos t) + 2)i + 10j + (3 + t )k, -?/2 < t < ?/2
A. T = (sin t)i + (cos t)k; N = (cos t)i - (sin t)k; B = j B. T = (sin t)i + (cos t)k; N = (cos t)i - (sin t)k; B = -j C. T = (-sin t)i + (cos t)k; N = (-cos t)i - (sin t)k; B = -j D. T = (-sin t)i + (cos t)k; N = (-cos t)i - (sin t)k; B = j
Solve the problem.The delivery of a drug (such as an antibiotic) through an intravenous line may be modeled by the differential equation 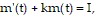 where m(t) is the mass of the drug in the blood at time
where m(t) is the mass of the drug in the blood at time  k is a constant that describes the rate at which the drug is absorbed, and I is the infusion rate. Let
k is a constant that describes the rate at which the drug is absorbed, and I is the infusion rate. Let  and
and 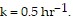 For what initial values
For what initial values
src="https://sciemce.com/media/4/ppg__tttt0613190828__f1q11g5.jpg" alt="" style="vertical-align: -4.0px;" /> are solutions increasing? decreasing? What is the equilibrium solution? A. increasing for A < 40 and decreasing for A > 40; m(t) = 40 B. increasing for A > 40 and decreasing for A < 40; m(t) = 40 C. increasing for A < 40 and decreasing for A > 40; m(t) = 0 D. increasing for A > 40 and decreasing for A < 40; m(t) = 0
Use transformations of either the graph of y = ln x or y = log x to graph the given equation.y = -3 ln x
A. 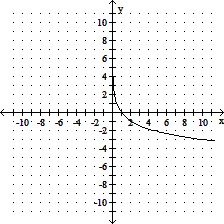
B. 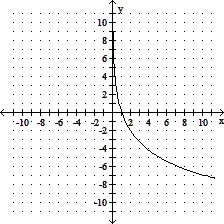
C. 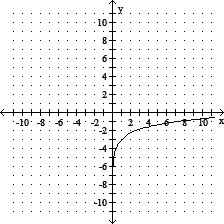
D. 
Find the grade point average. Round to the nearest tenth when necessary.The grades are given for a student for a particular semester. Find the grade point average. Assume the grade point values are A = 4, B = 3, C = 2, D = 1, and F = 0. C3 B1 C2 A2 B3
C3 B1 C2 A2 B3
A. 11 B. 2.7 C. 2.8 D. 2.2