Which of the following is true of the condition osteomyelitis? Select ALL that apply
It is caused by the normal skin bacterium, Staphylococcus aureus.
The condition involves inflammation of the bone, which is stimulated by osteoblasts releasing the chemical RANKL.
Osteoclasts are inhibited by the bacterium that causes the condition.
Prognosis for those affected is poor, even with excellent medical care.
__X__
It is caused by the normal skin bacterium, Staphylococcus aureus.
__X__
The condition involves inflammation of the bone, which is stimulated by osteoblasts releasing the chemical RANKL.
_____
Osteoclasts are inhibited by the bacterium that causes the condition.
_____
Prognosis for those affected is poor, even with excellent medical care.
You might also like to view...
The ribs are _____ to the sternum
a) lateral b) medial c) proximal d) distal e) superior
Structure D is a(n)
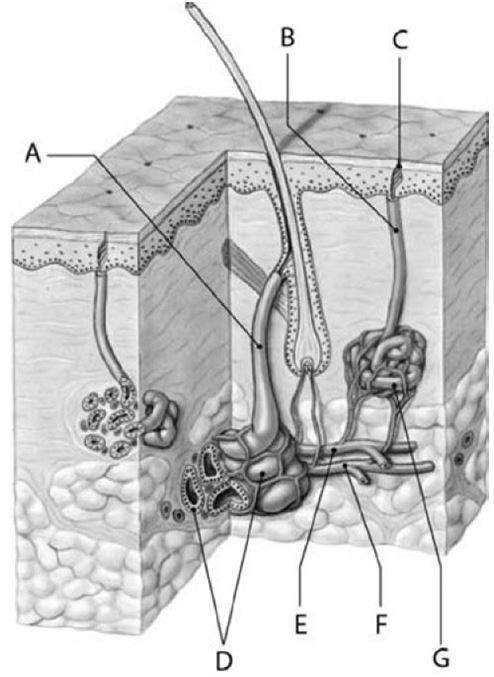
A) endocrine gland.
B) sebaceous gland.
C) merocrine gland.
D) apocrine gland.
E) unicellular gland.
P450 aromatase is responsible for feminization of the hypothalamus so that a female pattern of hormone secretion occurs
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Prions are pathogenic proteins that are linked to different neurodegenerative diseases. Investigations of some have indicated that normal cellular proteins and prions have the same amino acid sequence. How is this possible?
A. Though the primary structure is the same between the prion and the normal cellular protein, differences at higher levels (secondary or tertiary) alter protein activity. B. The amino acids of the prion must have more hydrophilic sections, causing it to interact with the lipids of the plasma membrane and disrupting cell activity. C. The amino acid sequence is not important to the function of the protein because protein function is completely determined by the pH of the environment. D. The double helix structure of proteins is easily altered by separating the nitrogenous bases holding the strands together, allowing for a protein to act as a prion.