Potential of Point-Charges: Point charges +4.00 ?C and +2.00 ?C are placed at the opposite corners of a rectangle as shown in the figure. What is the potential at point B due to these charges? (k = 1/4??0 = 8.99 × 109 N ? m2/C2) 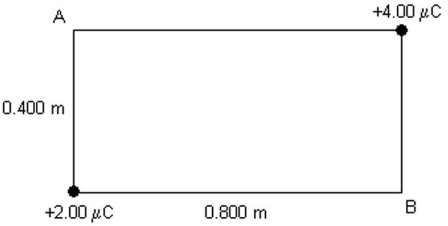
A. 8.99 kV
B. 11.2 kV
C. 89.9 kV
D. 899 kV
E. 112 kV
Answer: E
You might also like to view...
Molecular Speeds: What is the total translational kinetic energy of the gas in a classroom filled with nitrogen at 1.01 × 105 Pa at 20.7°C? The dimensions of the classroom are 4.60 m × 5.20 m × 8.80 m. The Boltzmann constant is 1.3806503 × 10-23 J/K, R = 8.31 J/mol ? K, and NA = 6.022 × 1023 molecules/mol.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
A hot-wire anemometer consists of a 5-mm-long, 5-?m-diameter platinum wire. The probe is operated at constant current of 0.03 amp. The electrical resistivity of platinum is 17 ??-cm at 20°C and increases by 0.385% per °C. (a)If the voltage across the wire is 1.75 volts, determine the velocity of the air flowing across it and the wire temperature if the free-stream air temperature is 20°C. (b)What are the wire temperature and voltage if the air velocity is 10 m/s? Neglect radiation and conduction heat transfer from the wire.
GIVEN • A hot wire in air • Wire diameter (D) = 5 m = 5 × 10–6 m • Wire length (L) 5 mm = 0.005 m • Current (I) = 0.03 A (constant) • Electrical resistivity (rel) = 17 W cm = 17 × 10–8 W m at 20°C and increases 0.385% per °C. • Air temperature (T?) = 20°C FIND (a) The air velocity (U?) and the wire temperature (Tw) if the voltage across the wire (Vel) =1.75V (b) The wire temperature (Tw) and voltage (Vel) if the air velocity (U?) = 10 m/s ASSUMPTIONS • Radiative heat transfer is negligible • Variation of Prandtl number with temperature id negligible PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.0251 W/(m K) Kinematic viscosity (?) = 15.7 × 10–6 m2/s Prandtl number (Pr) = 0.71 At 90°C: Pr = 0.71
A hot piece of iron is thrown into the ocean and its temperature eventually stabilizes. Which of the following statements concerning this process is correct? (There may be more than one correct choice.)
A) The change in the entropy of the iron-ocean system is zero. B) The entropy gained by the iron is equal to the entropy lost by the ocean. C) The entropy lost by the iron is equal to the entropy gained by the ocean. D) The ocean gains more entropy than the iron loses. E) The ocean gains less entropy than the iron loses.
The part of the electromagnetic spectrum most absorbed by water is
A) infrared. B) red. C) cyan. D) all about equally.