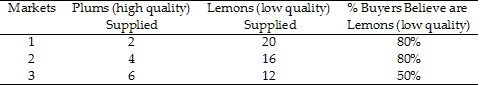
 Table 9.4 represents 3 markets for used motorcycles. Which of the markets in Table 14.4 are in equilibrium?
Table 9.4 represents 3 markets for used motorcycles. Which of the markets in Table 14.4 are in equilibrium?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. 3 only
D. 1 and 3
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
If a country's population grows at the same rate as its real GDP, then real per capita GDP:
a. grows at an increasing rate. b. grows at a constant rate. c. doesn't change. d. decreases at a decreasing rate. e. decreases at a constant rate.
Perfectly competitive firms ____ earn zero economic profit in long-run equilibrium because ____
a. always; firms in perfectly competitive industries always maximize output and so flood the market until the equilibrium price of output is driven to zero b. sometimes; the demand curve for an individual perfectly competitive firm may or may not cross the company's long-run average total cost curve at its lowest point c. always; firms enter whenever their economic profit is positive and exit whenever it's negative, so in long-run equilibrium economic profit must always be zero d. never; no firm would be willing to produce if it received zero economic profit
A monopolist is currently hiring 5,000 units of labor. At this level, the marginal revenue of output is $10, the (fixed) wage rate is $300, and the marginal product of labor is 50. In order to maximize profit, the firm should
A. hire more labor because the next unit of labor increases profit by $500. B. hire more labor because the next unit of labor increases profit by $200. C. hire less labor because the last unit of labor added more to total cost ($300) than to total revenue ($10). D. keep the level of employment the same because the firm is earning a profit of $100,000.
In long-run equilibrium, which of the following is not equal to price for a perfectly competitive firm?
A. short-run average variable cost B. long-run average total cost C. short-run marginal cost D. short-run average total cost