Use the following graph for a market to answer the question below.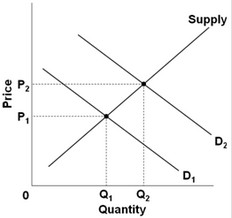 Which of the following would best explain why the shift in demand from D1 to D2 would cause price to rise from P1 to P2?
Which of the following would best explain why the shift in demand from D1 to D2 would cause price to rise from P1 to P2?
A. After the shift in the demand, there would be a surplus at price P2.
B. After the shift in the demand, there would be a shortage at price P1.
C. After the shift in the demand, there would be a surplus at price P1.
D. After the shift in the demand, there would be a shortage at price P2.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Refer to Figure 8.1. If each player cooperated with one another rather than playing their dominant strategies, the economic pie would grow by
A) $0. B) $280. C) $490. D) $560.
Figure 5-8

A. A, C. B. B, D. C. C, B. D. A, B.
The firm whose short-run cost curves are given in Exhibi has a long-run fixed cost of
A. $0. B. $2. C. $3. D. $4.
Suppose the factory Afro-Puffs Inc. produces wigs. As a by-product of this wig production, they also produce dangerous emissions of toxic gases (as a result of the strong glue used to hold the hair in place). The De-Lite car factory, down the road, experiences a negative externality from this production process. Suppose that the supply curve (private marginal costs) for the wig factory is X = (2/5)P - 2, and it faces a market demand of X d = 15 - P/2. The marginal damages caused by the production of wigs can be written as X = P - 1/2.
(a) Find the equilibrium price and quantity in the market for wigs. (b) Find the socially optimal level of wigs and the corresponding price. (c) How much should the wig factory be taxed per wig?