For a given supply curve, an increase in demand will typically
a. increase price, but quantity could change in either direction
b. increase quantity, but price could change in either direction
c. increase price but leave quantity unchanged
d. decrease both quantity and price
e. increase both quantity and price
E
You might also like to view...
Refer to the below graph of the market for low-skilled labor. Sd is the supply of domestic resident workers, and St is the total supply of labor including undocumented workers. If there are illegal immigrants in the market, how many legal residents will be employed?
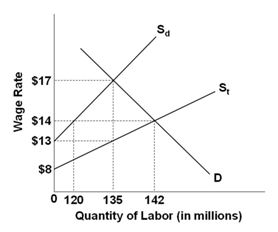
A. 15M
B. 120M
C. 135M
D. 22M
Two competing firms in a duopoly must decide whether or not to offer consumers a coupon for their good. The payoff matrix above represents the daily profit available to the firms under the different coupon strategies
a. What strategies and payoffs are represented by quadrant A? b. What strategy will Firm 1 pursue if it believes that Firm 2 is offering a coupon? c. What quadrant represents the equilibrium that will result if the firms act independently (compete)? d. What quadrant represents the equilibrium that will result if the firms successfully collude?
Which statement is correct? The long-run supply curve for a purely competitive:
A. increasing-cost industry is perfectly elastic. B. increasing-cost industry is upsloping. C. decreasing-cost industry is upsloping. D. increasing-cost industry is less elastic than the industry's short-run supply curve.
A rightward shift of the AD curve in the very steep upper part of the short-run AS curve will:
A. increase real output by more than the price level. B. increase the price level by more than real output. C. reduce real output by more than the price level. D. reduce the price level by more than real output.