Suppose that the equilibrium price of apples decreases and the equilibrium quantity of apples increases. This is best explained by:
A. an increase in the demand for apples.
B. an increase in the supply of apples.
C. a decrease in the supply of apples.
D. a decrease in the demand for apples.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Suppose there is a decline in the demand for the product labor is producing. Furthermore, the price of capital, which is complementary to labor, increases. Thus, the demand for labor
A. will decrease. B. will increase. C. may either increase or decrease. D. will not change.
The benevolent social planner would like to see people take
A) all possible precautions. B) all cost-justified precautions. C) only cost-justified precautions. D) both b and c
When the U.S. dollar rises in value, this tends to _____ our imports and ______ our exports.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
Refer to the diagram where D and S are the United States' demand for and supply of Swiss francs. At the equilibrium exchange rate, E, the United States' balance of payments is in equilibrium. Given a change in demand from D to D', the United States could maintain the dollar price of Swiss francs by:
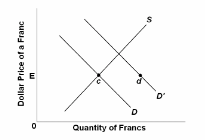
A. shifting the S curve to the right through the use of domestic expansionary policies.
B. instituting exchange controls to ration Ed Swiss francs to U.S. importers who want Ec
francs.
C. using international monetary reserves to cover the Ec shortage of Swiss francs.
D. using international monetary reserves to cover the cd shortage of Swiss francs.