Labeling.Label the parts of the model animal cell.
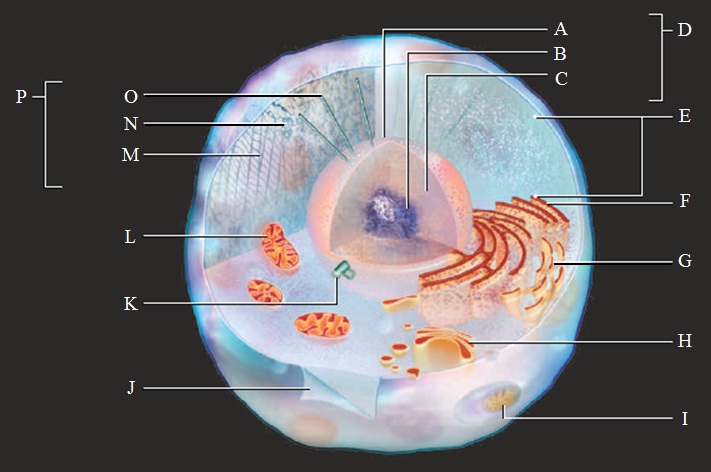
A. Nuclear envelope
B. Nucleolus
C. DNA in nucleoplasm
D. Nucleus
E. Ribosomes
F. Rough ER
G. Smooth ER
H. Golgi body
I. Lysosome
J. Plasma membrane
K. Pair of centrioles
L. Mitochondrion
M. Intermediate filaments
N. Microfilaments
O. Microtubules
P. Cytoskeleton components
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
F. 6
G. 7
H. 8
I. 9
J. 10
K. 11
L. 12
M. 13
N. 14
O. 15
P. 16
You might also like to view...
Given the DNA template shown in the figure above, which of the following bases would you find in a complementary RNA strand and where would they be synthesized?
A) A-A-A-A-A; nucleus B) U-U-U-U-U; nucleus C) A-A-A-A-A; ribosome D) U-U-U-U-U; ribosome
Which of the following is true?
A) Mutations that inactivate tumor suppressor genes are important in cancer. B) Cancer is a single disease with one underlying molecular cause. C) Uncontrolled cell growth alone is sufficient for the development of cancers. D) Cancer is a single disease resulting from a common set of mutations.
This chapter discussed speciation by genetic divergence following geographic isolation, which is expected to lead to reduced gene flow, a process known as allopatric speciation
A more controversial form of speciation is the genetic divergence of populations without physical isolation, a process known as sympatric speciation. Can you envision a mechanism or process that would permit two coexisting populations of the same species to begin to diverge without being isolated from one another?
Which of the following devices is used for PCR?
A) an electrophoresis chamber B) a gene gun C) a DNA sequencer D) a thermocycler E) a nucleic acid synthesis machine