In what phase of the general adaptation syndrome reaction to stress does the body adapt to its high state of arousal in an attempt to cope with the stressor?
A) alarm
B) resistance
C) exhaustion
D) fight-or-flight
B) resistance
You might also like to view...
Many adolescent males
a. are very dissatisfied with their bodies. b. would like to lose weight. c. would like to build their muscle mass by adding weight. d. are less satisfied with their bodies than are adolescent females.
The expression "the squeaky wheel gets the grease" is associated with which of the following concepts?
a. individualism b. Western ideology c. collectivism d. introspection
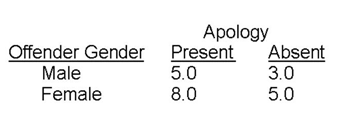
Describe the research design the researcher used, including the type of variables, and identify the conditions that are created using factorial combination.
A researcher examined whether people's responses to injustice depend on whether the offender in a hypothetical scenario is a male or a female, and whether the offender apologized (or not) after the offense. Participants were randomly assigned to the gender of the offender condition (female, male) and apology condition (present, absent).
Participants read a hypothetical scenario in which a person (male or female) acted unjustly and the action results in severe harm. Half of the participants read that the offender apologized; the other half read the same scenario except no apology was mentioned. Participants then rated the extent to which they would forgive the offender using a 0 (no forgiveness) to 9 (complete forgiveness) rating scale. The researcher predicted that participants' forgiveness would be greater following an apology compared to the apology-absent condition. The researcher also predicted that the gender of the offender would have no effect on forgiveness.
The researcher observed the following means:
In the first year of life, the main causes of death are
A. acute illness and sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS). B. accidents and congenital abnormalities. C. cancer, especially leukemia, and sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS). D. sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) and congenital abnormalities.