A monopoly incurs a marginal cost of $1 for each unit produced. If the price elasticity of demand equals -2.0, the monopoly maximizes profit by charging a price of
A) $1.00.
B) $1.50.
C) $2.00.
D) $3.00.
C
You might also like to view...
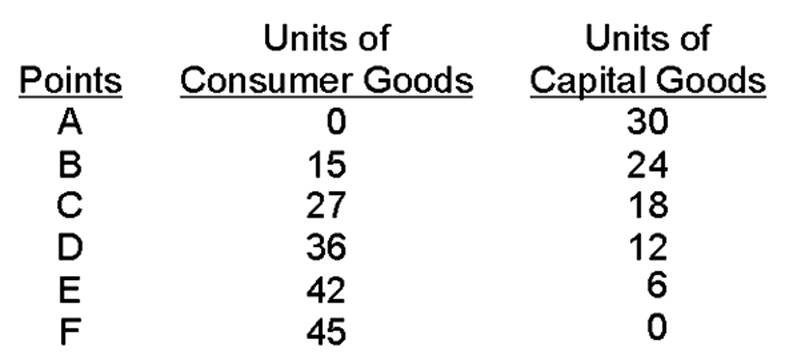
In the table above, points A through F represent _______________________ of resources.
Why might it be a bad idea to engage in first-degree price discrimination?
A. Price discrimination is illegal and can lead to lawsuits and lost customers. B. The information needed does not exist and scarce resources should not be used searching for it. C. Price discrimination in any form is not viable for most companies as a way to increase profits. D. The information needed can be costly and can lead to decreased profits for the company.
If the price of its product falls below the minimum point on the AVC curve, the best a perfectly competitive firm can do is to
A) keep producing and incur an economic loss equal to its total variable cost. B) keep producing and incur an economic loss equal to its total fixed cost. C) shut down and incur an economic loss equal to its total variable cost. D) shut down and incur an economic loss equal to its total fixed cost.
Suppose that in each of four successive years producers sell more of their product and at lower prices. This could be explained:
A. by small annual increases in supply accompanied by large annual increases in demand. B. in terms of a stable supply curve and increasing demand. C. in terms of a stable demand curve and increasing supply. D. as an exception to the law of supply.