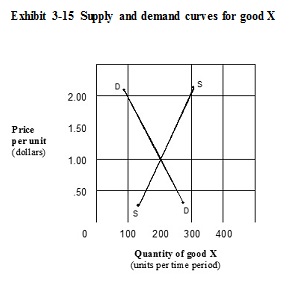
In the market shown in Exhibit 3-15, the equilibrium price and quantity of good X are:
A. $0.50, 250.
B. $2.00, 300.
C. $2.00, 100.
D. $1.00, 200.
D. $1.00, 200.
You might also like to view...
Which of the following has been a problem faced by the FDIC in its provision of federal deposit insurance?
A) a relatively low number of bank failures each year, which has reduced the need for deposit insurance B) moral hazard arising from the tendency for the highest-risk banks to be those most interested in obtaining deposit insurance in the first place C) adverse selection arising from the tendency for banks to take on more risk after they receive deposit insurance D) moral hazard arising from the tendency for banks to take on more risk after they receive deposit insurance
As a country that has a bowed-out production possibilities frontier produces more of one good, the opportunity cost of a unit of that good ________
A) might increase or decrease B) remains the same C) increases D) decreases
How do firms and households interact within the context of the circular flow model?
What will be an ideal response?
A monopolist is maximizing profit at an output rate of 100 units per week. At this output rate, the price that its customers are willing and able to pay is $8 per unit, average total cost is $5 per unit, and marginal cost is $6 per unit. It may be
concluded that at this monthly output rate, marginal revenue is A) $5 per unit, and the monopolist earns zero economic profits. B) $6 per unit, and the monopolist earns economic profits of $200 per week. C) $6 per unit, and the monopolist earns economic losses of $100 per week. D) $6 per unit, and the monopolist earns economic profits of $300 per week.