Externalities can be corrected by each of the following except
a. self-interest.
b. moral codes and social sanctions.
c. charity.
d. normal market adjustments.
d
You might also like to view...
Suppose that a government agency is trying to decide between two pollution reduction policy options. Under the permit option, 100 pollution permits would be sold, each allowing emission of one unit of pollution. Firms would be forced to shut down if they produced any units of pollution for which they did not hold a permit. Under the pollution tax option, firms would be taxed $250 for each unit of pollution emitted. The regulated firms all currently pollute and face varying costs of pollution reduction, though all face increasing marginal costs of pollution reduction. Suppose the regulators chose the permit policy instead of the tax policy. What might explain that decision?
A. Permit auctions raise more revenue than do taxes. B. The permit policy will reduce pollution by more than would the tax policy. C. The permit policy allows regulators to achieve reduction goals without having detailed knowledge about firms' abatement costs. D. Firms prefer the permit policy because it allows them to choose the least-costly reduction technology.
Refer to the figure below. In response to gradually falling inflation, this economy will eventually move from its short-run equilibrium to its long-run equilibrium. Graphically, this would be seen as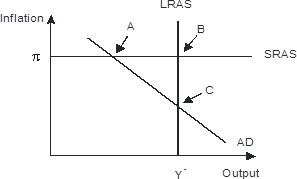
A. long-run aggregate supply shifting leftward B. Short-run aggregate supply shifting downward C. Aggregate demand shifting rightward D. Aggregate demand shifting leftward
The difference between the market price of a new car used by a firm and the market price of the same car one year later is known as
A) economic depreciation. B) physical depreciation. C) economic deterioration. D) physical deterioration.
In long-run macroeconomic equilibrium
A) real GDP equals potential GDP. B) the price level is fixed and aggregate demand determines real GDP. C) real GDP and the price level are determined by short-run aggregate supply and aggregate demand and long-run aggregate supply is irrelevant. D) real GDP is less than potential GDP.