Refer to the diagram and list of assumptions. The elimination of gender discrimination:
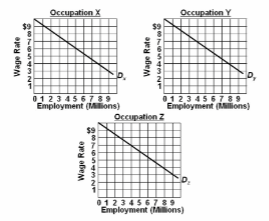
(1) the labor force is comprised of 9 million men and 9 million women workers;
(2) the economy has 3 occupations, X, Y, and Z, each having identical demand curves for
labor; (3) men and women workers are homogeneous with respect to their labor-market
capabilities; (4) women are discriminated against by being excluded from occupations X and Y
and are confined to Z; and (5) aside from discrimination, the economy is competitive, and
workers seek to maximize their earnings.
A. may either increase or reduce real domestic output, depending on what happens to the
level of wages.
B. will increase real domestic output.
C. will have no effect on real domestic output.
D. will reduce real domestic output.
B. will increase real domestic output.
You might also like to view...
Which of the following occur when a person maximizes utility? I. The marginal utility of each good bought is equal. II. The highest level of utility is attained. III. All of a person's budget is spent
A) I and II B) I and III C) II and III D) I, II and III
Refer to Table 2-11. What is China's opportunity cost of producing one digital camera?
A) 0.04 pounds of wheat B) 4 pounds of wheat C) 25 pounds of wheat D) 40 pounds of wheat
What is true about threats in the game in Scenario 13.15?
A) Simple can change the equilibrium by means of a credible threat; Boring cannot. B) Boring can change the equilibrium by means of a credible threat; Simple cannot. C) Boring can change the equilibrium by means of a credible threat only if it can move before Simple. D) Simple can change the equilibrium by means of a credible threat only if it can move before Boring. E) Neither firm has a credible threat with which to change this equilibrium.
Suppose a law firm negotiates a very low price for each of its 1000 employees to be members at the athletic club that is located next to the law firm. Which of the following is not likely to be true?
A. If the typical individual gym membership costs $50 per month, the law firm should expect to save $50,000 per month in wages. B. The firm can likely negotiate a lower per person price at the gym than each employee could negotiate alone. C. In the long run, the law firm will probably attract workers who value the gym benefit the most. D. The law firm can pay its workers less than a comparable law firm that does not offer the gym benefit. E. Some employees will take advantage of the gym benefit, while others will not.