At which type of convergent plate boundary did the Himalaya mountain belt form, and why?
a. at a continental-continental convergent boundary because when one of the continental plates subducted under the other continental plate, debris was scraped off the top of the plate and that formed the Himalayas
b. at an oceanic-continental convergent boundary because when the oceanic plate subducted under the continental plate, a volcanic chain was formed which later cooled and became the mountains now known as the Himalayas
c. at an oceanic-oceanic boundary because when the two oceanic plates collided, they crumpled up at the zone of collision to form a landmass with mountains
d. at an oceanic-continental convergent boundary because when the oceanic plate subducted under the continental plate, debris was scraped off the top of the oceanic plate and formed the Himalayas
e. at a continental-continental convergent boundary, because the two continental plates buckled and thickened vertically when they collided
e. at a continental-continental convergent boundary, because the two continental plates buckled and thickened vertically when they collided
You might also like to view...
If Uranium-234 decays via alpha emission, what is the likely product of radioactive decay? (U, atomic no. = 92)
A. 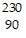 Th
Th
B. 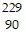 Th
Th
C. 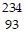 Np
Np
D. 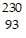 Np
Np
E. none of the above
A newly discovered conventional oil reserve is most likely to be found
A) beneath the sea floor. B) in the Middle East. C) in Texas. D) in the Appalachian Mountains.
Which type of convergent plate boundary results in a chain of submarine volcanoes?
A) oceanic-oceanic B) continental-continental C) continental-oceanic D) ridge-hot spot
The most effective form of wave erosion is ____
a. deflation b. hydraulic action c. abrasion d. corrosion