Repeat Problem 9.27 using the following data:
where at T = 300 K
vS = 5.3 V + 7 cos(?t) mV
? = 377 rad/s R = 4.6 k?
Problem 9.27
The silicon diode shown in Figure P9.27 is described by:
where at T = 300 K
vS = 4.2 V + 110 cos(?t)mV
? = 377 rad/s R = 7 k?
Determine the current iD at the operating point Q:
a. Using the diode offset model.
b. By graphically solving the circuit characteristic (i.e., the DC load-line equation) and the device characteristic (i.e., the diode equation).
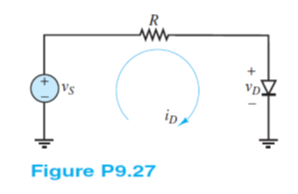
Suppress the AC component of the source voltage. Construct the DC equivalent circuit using the threshold (or offset voltage model). The Q point is at the intersection of the device (diode) characteristic and the circuit characteristic given by the KVL below. Here, the device characteristic is approximated by the threshold voltage model giving the approximate Q point at the upper right.
The DC source voltage will tend to make the diode conduct. Assume the diode is on.
Then:
You might also like to view...
? What should be done if a dimension cannot be found on a drawing?
What will be an ideal response?
What are the three Rs of robotics, and what do they mean?
What will be an ideal response?
When light strikes a photoresistor, its resistance is __________.
A. low B. high
The charging scheme used in Figure P2.11 is an example of a constant-current charge cycle. The charger voltage is controlled such that the current into the battery is held constant at 40 mA, as shown in Figure P2.11. The battery is charged for 6 h.
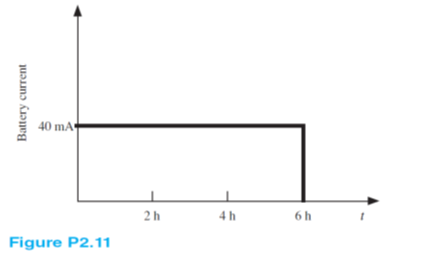
Find:
a. The total charge delivered to the battery.
b. The energy transferred to the battery during the charging cycle.
Hint: Recall that the energy, w, is the integral of power, or P = dw/dt.