Oxygen at T=400 K and P=2 atm flows into an adiabatic, reversible nozzle operating at steady-state. The stream has a negligible velocity as it enters the nozzle but is ejected at a high velocity. The exiting oxygen is at P=0.5 atm. You may assume that oxygen is an ideal gas with constant Cp*=(7/2)R. On a mass basis, this is equivalent to CP = 0.909 kJ/kg-K.
A) Find the change in entropy of the universe resulting from this process.
B) Find the temperature and velocity of the oxygen leaving the nozzle.
C) Find ?U for the oxygen in J/mol.
In a reversible process the total entropy of a system plus its surrounding is unchanged, so ??S_univ=0. Since the process is adiabatic, steady state and reversible, the change in entropy of the gas is also 0.
Apply the change in entropy of an ideal gas equation to calculate Tout:
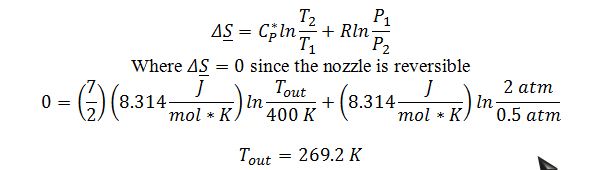
Apply energy balance to the adiabatic, steady state nozzle with a negligible initial velocity:
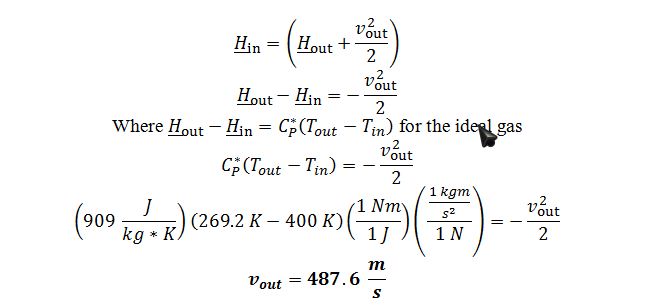
C) Apply definition of change in internal energy for ideal gas:
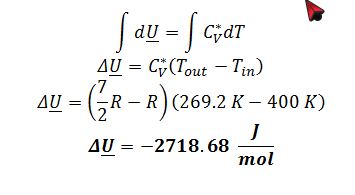
You might also like to view...
A branch circuit within a branch circuit is known as ____________________.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
Which part of a synchronizer is splined to a shaft?
A) Speed gear B) Synchronizer sleeve C) Hub D) Synchronizer blocker ring
There are 640 acres in a square mile. How many square miles are there in 80 acres?
a. 1/16 b. 1/8 c. 1/4 d. 1/2
How much heat is required to increase the temperature of 20 lb of water from 32°F to 212°F?
A) 20 lb × 0.5 × 180°F = 1,800 BTU B) (20 × 144 ) + (20 × 180 ) + (20 × 970 ) = 25,880 BTU C) 212°F - 32°F = 180 BTU D) 20 lb × 180°F = 3,600 BTU