Compare the results of Problem 13.21(a) and (c) with Problem 13.22(a) and (c).
Computer Study—comparison of approximate analysis with exact analysis.
Consider the structure in Figure P13.21. (a) Use approximate analysis to compute the
reactions and draw moment diagram for the column AB and draw the approximate deflected shape of the frame. (b) Determine truss bar forces. All truss joints are pinned. (c) Compare the results with the exact analysis using a computer software. Truss member properties are A
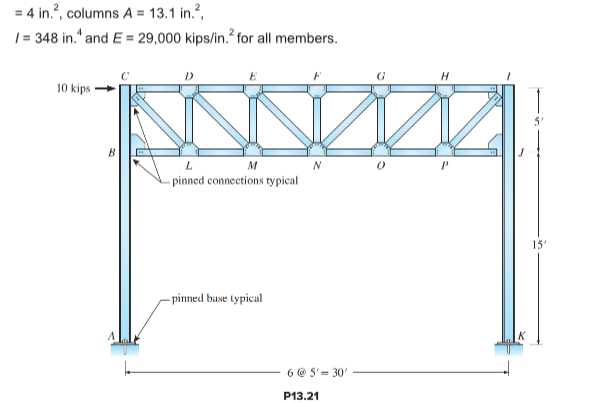
Computer Study—comparison of approximate analysis with exact analysis.
Consider the structure in Figure P13.22. (a) Use approximate analysis to compute the
reactions and draw moment diagram for the column AB and draw the approximate deflected shape of the frame. (b) Determine truss bar forces. All truss joints are pinned. (c) Compare the results with the exact analysis using a computer software. Truss member properties are A
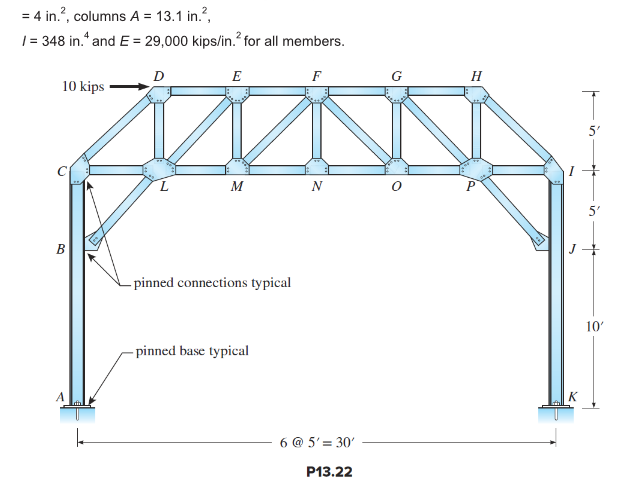
The analysis approach is the same for both problems P13.21 and P13.22. Both structures
have same boundary conditions of pinned bases, and both are symmetric in geometric and
material properties, the same assumption applied to both: lateral load is divided equally to the
columns. Their analysis results are differ due to the knee brace. The remaining results are
consistent with similar truss bar forces for the middle 2/3 of the truss.
Comparison of problems P13.21 and P13.22 generate different results in the column
moments and shears, and is primarily due to the knee brace in P13.22. The truss frame in
problem P13.22 is 5 ft taller and it’s lateral load is applied at 20ft up from the base compared
with the parallel chord truss in problem P13.21, which has a height of 15 ft with it’s lateral
load applied at the 15 ft top chord. It would appear at first that the moment at joint B would
have a larger magnitude in the taller frame in P13.22, however the knee brace brings the
column height to 10 ft reducing the moment arm. Results for moment at B:
Mb = 50 ft -k in P13.22 vs Mb = 75 ft-k in P13.21, and horizontal force component of the knee
brace = 15k vs 20 k in the bottom chord of the parallel chord truss, resulting in a 33.3%
increase in moment and horizontal force at B.
You might also like to view...
A pitot tube monitors and meters fluid and steam in _____ pipes.
a. large b. small c. static d. bind flanged
If someone is practicing three point contact they will be:
a. using a special type of fastener b. in contact with a machine with two hands and one foot or two feet and one hand c. be in contact with a machine with a hand, foot and a safety harness d. be in a machine's seat with a three point seat belt on
Describe and give an example of hard conversion.
What will be an ideal response?
What is the difference between cutting plane lines and viewing plane lines?
A. Cutting plane lines are only used where a portion of an object is completely cut away. B. Viewing plane lines are thicker than cutting plane lines. C. Cutting plane lines are thicker than viewing plane lines. D. Viewing plane lines are used to identify where a section is taken. E. none of the above