Under perfect competition
A) information about prices is hard to obtain.
B) there is a maximum number of firms that can enter the market.
C) if a firm exits the market, price will rise.
D) transaction costs are low.
D
You might also like to view...
When comparing the composition of world trade in the early 20th century to the early 21st century, we find major compositional changes. These include a relative decline in trade in agricultural and primary-products (including raw materials)
How would you explain this in terms of broad historical developments during this period?
Big Waves is a large water park. Suppose the individual demand for entrance into Big Waves is Qd = 50 - (2 × P) and each consumer has the same demand. Big Waves has a constant marginal cost of $5 per consumer. If Big Waves charges a single entry price to each consumer, what is the profit-maximizing price per consumer?
A) $25 B) $15 C) $20 D) $10
If a country is in a major recessionary phase of the business cycle, one can expect that its currency will
a. revalue. b. devalue. c. appreciate. d. depreciate.
The following payoff matrix shows the outcomes for the United States and Russia from relying on conventional weapons versus atomic weapons in a military conflict. The percentages refer to the fraction of the population that would die.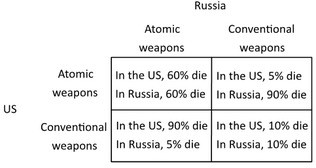 This situation above illustrates a positional externality because:
This situation above illustrates a positional externality because:
A. using atomic weapons improves each country's outcome but hurts the other country. B. the game does not have a Nash equilibrium. C. using atomic weapons is a dominated strategy. D. no matter what kind of weapons each country chooses, many people will die.