What would be the impact of a minimum wage that is set below the equilibrium wage that would otherwise prevail in the labor market?
What will be an ideal response?
This would have no impact on the labor market. The reason is that the market is already paying workers above what the minimum wage requires. The only way for a minimum wage to have any practical effect on the labor market is for it to be set above the equilibrium wage rate.
You might also like to view...
Keynes' theory of consumption predicts that the aggregate saving rate
A) increases as society becomes richer. B) falls as society becomes richer. C) is constant in the long-run. D) falls with higher incomes in a cross-section of income.
The first welfare theorem:
A. tells us that, in a general equilibrium with perfect competition, the allocation of resources is Pareto efficient. B. clarifies how the "invisible hand" of the market guides people toward socially undesirable choices. C. tells us that a general equilibrium with perfect competition is not Pareto efficient. D. is also the only welfare theorem.
Based on the figure below. Starting from long-run equilibrium at point C, a decrease in government spending that decreases aggregate demand from AD1 to AD will lead to a short-run equilibrium at__ creating _____gap.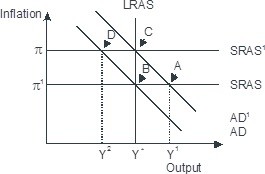
A. B; no output B. D; an expansionary C. B; recessionary D. D; a recessionary
Outsourcing is a term increasingly used to refer to the act of:
A. hiring illegal immigrants. B. replacing relatively expensive American workers with low-wage workers overseas. C. importing raw materials into the United States from other countries. D. exporting final goods to other countries.