For a specific element, photons of how many different energies could be absorbed by electrons to jump from the n = 1 to n = 5 level?
a. 20
b. 10
c. 6
d. 1
e. 4
d
You might also like to view...
An electronic device is cooled by passing air at 27°C through six small tubular passages in parallel drilled through the bottom of the device in parallel as shown. The mass flow rate per tube is 7 × 10–5 kg/s. Heat is generated in the device resulting in approximately uniform heat flux to the air in the cooling passage. To determine the heat flux, the air outlet temperature is measured and found to be 77°C. Calculate the rate of heat generation, the average heat transfer coefficient, and the surface temperature of the cooling channel at the center and at the outlet.
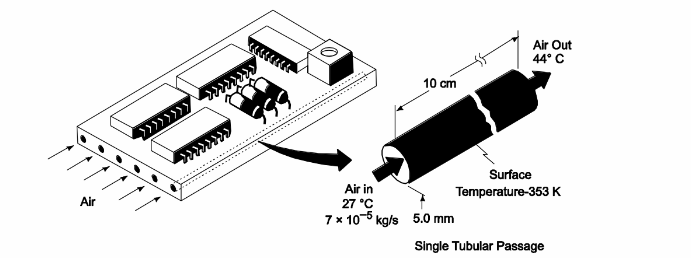
GIVEN
• Air flow through small tubular passages as shown above
• Air temperature
? Entrance (Tb,in) = 27°C
? Exit (Tb,out) = 77°C
• Mass flow rate per passage (m )= 7 × 10–5 kg/s
• Number of passages (N) = 6
FIND
(a) The rate of heat generation ( Q
G) (b) The average heat transfer coefficient ( h c) (c) Cooling channel surface temperature at the center (Ts,c) (d) Cooling channel surface temperature at the outlet (Ts,out)
ASSUMPTIONS
• Steady state
• Uniform heat generation
• Uniform heat flux to the air
• Viscosity variation is negligible
• Heat transfer coefficient is approximately constant axially
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
for dry air at the average bulk temperature of 52°C
Specific heat (c) = 1016 J/(kg K) ]
Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.0273 W/(m K)
Absolute viscosity (?) = 19.593 × 10–6 (Ns)/m2
Prandtl number (Pr) = 0.71
At every instant the ratio of the magnitude of the electric to the magnetic field in an electromagnetic wave in vacuum is equal to
a. the speed of radio waves. b. the speed of light. c. the speed of gamma rays. d. all of the above. e. only (a) and (b) above.
Some species of whales can dive to depths of one kilometer. What is the total pressure they experience at this depth? (?sea = 1 020 kg/m3 and 1.01 × 10^5 N/m2 = 1 atm.)
a. 9.00 atm b. 90.0 atm c. 100 atm d. 111 atm e. 130 atm
What is the solar wind?
a. strong radiation that comes from the Sun b. similar to winds on Earth, but faster and stronger c. similar to winds on Earth, but less dense and weaker d. atoms and particles ejected from the Sun at high speed e. strong winds on the surface on the sun due to large temperature differences