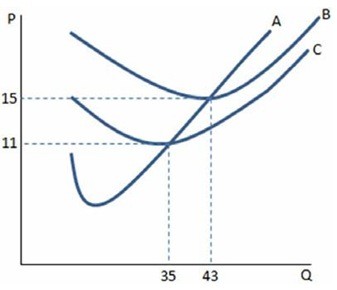
 If a firm in a perfectly competitive market faces the cost curves in the graph shown and observes a market price of $10, the firm:
If a firm in a perfectly competitive market faces the cost curves in the graph shown and observes a market price of $10, the firm:
A. can make positive profits by producing where MC = MR.
B. cannot make positive profits and should shut down in the short run.
C. can make positive profits by producing more than 43 units.
D. should continue to operate in the short run, but plan to exit in the long run.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
The existence of unemployment can be illustrated on a production possibilities curve by a(n)
A. point below or inside the surface of the curve. B. inward shift of the curve. C. movement along the curve. D. outward shift of the curve.
An example of "investment" in computing real GDP using the expenditure approach is the purchase of
A) a new set of tools by an auto mechanic, for use in repairing cars. B) 100 shares of IBM stock. C) a 100 year old house by a married couple. D) computer chips by Dell to put in their personal computers.
The authors explain that a firm earning a zero economic profit in the long run has earned a competitive return on their investment. What do they mean by "competitive" return in this context?
A) The firm's return could only be earned under perfect competition and would be smaller under imperfect competition. B) The firm's return is at least as larger as the returns earned by other firms. C) The firm's return is at least as larger as could be earned in another investment. D) The firm's return is negative, which initiates stronger competition among firms in the market.
Airlines are __________ than they were before deregulation
a. more dangerous b. more concentrated c. higher priced d. flying fewer miles e. much more profitable