One of the fundamental problems in economics is how to deal with ________.
limited resources but practically unlimited economic desires
limited resources and limited desires
unlimited resources and limited desires
unlimited resources and unlimited desires
limited resources but practically unlimited economic desires
You might also like to view...
New Keynesian inflation dynamics predicts that an increase in aggregate demand will generate, in chronological order
A) a rightward movement along a horizontal short-run aggregate supply curve, a short-run increase in real GDP, an upward shift in the short-run aggregate supply curve, and an increase in the price level. B) a leftward movement along a horizontal short-run aggregate supply curve, a short-run decline in real GDP, a downward shift in the short-run aggregate supply curve, and a decrease in the price level. C) an leftward shift in a vertical short-run aggregate supply curve, a short-run decline in real GDP, an upward movement along the short-run aggregate supply curve, and an increase in the price level. D) a rightward shift in a vertical short-run aggregate supply curve, a short-run increase in real GDP, an upward movement along the short-run aggregate supply curve, and an increase in the price level.
The extent to which investment spending changes with changes to income is called the:
A) marginal propensity to consume. B) marginal propensity to save. C) marginal propensity to import. D) marginal propensity to invest.
In response to the recession of 2008-2009, the United States
a. increased government spending as a share of the economy and enlarged the size of the budget deficit. b. reduced government spending as a share of the economy and shifted the budget toward a surplus. c. increased government spending as a share of the economy and shifted the budget toward a surplus. d. reduced government spending as a share of the economy and enlarged the size of the budget deficit.
Based on this graph, the multiplier effect shifts the aggregate demand curve from ______.
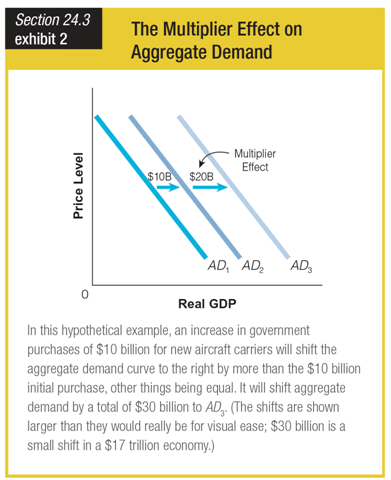
a. AD1 to AD2
b. AD2 to AD1
c. AD2 to AD3
d. AD1 to AD1