The country of Myrule has produced the following quantity of gauges and potatoes, with the price of each listed in dollar terms.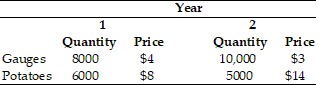 (a)Using Year 1 as the base year, what is the growth rate of real GDP from Year 1 to Year 2? (b)Based on the GDP deflator, what is the inflation rate from Year 1 to Year 2?
(a)Using Year 1 as the base year, what is the growth rate of real GDP from Year 1 to Year 2? (b)Based on the GDP deflator, what is the inflation rate from Year 1 to Year 2?
What will be an ideal response?
| (a) | Real GDP for Year 1 = Year 1 quantities at Year 1 prices = (8000 × $4) + (6000 × $8) = $80,000. |
Growth rate of real GDP = 0%
| (b) | Nominal GDP for Year 1 = Year 1 quantities at Year 1 prices = (8000 × $4) + (6000 × $8) = |
Nominal GDP for Year 2 = Year 2 quantities at Year 2 prices = (10,000 × $3) + (5000 × $14) = $100,000.
GDP deflator = nominal GDP/real GDP
GDP deflator in Year 1 = $80,000/$80,000 = 1.
GDP deflator in Year 2 = $100,000/$80,000 = 1.25.
Inflation rate = [(1.25/1) - 1] × 100% = 25%.
You might also like to view...
When we compare PAE and actual output (Y) the macroeconomic variable we generally use to directly assess their equivalence is:
A. unemployment. B. interest rates. C. inventories. D. capital expenditure.
Job amenities: a. have no impact on the supply of labor
b. are not part of the compensation workers receive from employers. c. help determine the position of the labor supply curve. d. never affect the monetary wages paid to workers.
If an increase in the growth rate of AD leads to an increase in real GDP in the short run: a. the increase in AD was correctly anticipated
b. the increase in AD was greater than anticipated. c. the increase in AD was less than anticipated. d. the increase in AD could have been any of the above.
Economists think of products as being in the same market if they
A. are traded in the same geographic location. B. cannot be substituted for other goods and services. C. are highly interchangeable. D. produced by companies that complete with each other.