If a dominant firm charged a very high price for its product, the firm ________ face scrutiny by the European Union competitive laws and ________ face scrutiny by the United States antitrust agencies.
A) would not necessarily; would
B) would; would not necessarily
C) would not necessarily; would not necessarily
D) would; would
B) would; would not necessarily
You might also like to view...
One reason why, in reality, prices are sticky in the short run is because
A) there are often costs to firms from changing prices. B) purely competitive firms have no control over the price of their product and therefore cannot change the price, even if the market warrants a price change. C) in the short run, the cost to changing prices always outweighs any benefit. D) firms do not have time to react to macroeconomic shocks in the short run.
Refer to the accompanying figure. The opportunity cost of making an additional salad: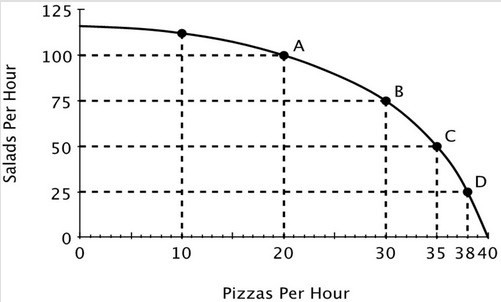
A. decreases as the number of salads increases. B. increases as the number of salads increases. C. decreases as the number of pizzas decreases. D. remains constant regardless of how many salads are made.
A budget deficit is incurred whenever:
A. Tax revenues fall short of expenditures over the fiscal year. B. Discretionary fiscal spending is used to achieve macro equilibrium. C. The U.S. Treasury engages in refinancing activities. D. The government uses fiscal policy.
The shorter is the interval between firms' price adjustments,
A. a given unexpected increase in aggregate demand will cause a smaller increase in the price level in the short run. B. a given unexpected increase in aggregate demand will cause a larger increase in output. C. the greater is the scope for activist policies to stabilize the economy. D. the smaller is the scope for activist policies to stabilize the economy.