Refer to the diagram. At output level Q 1:
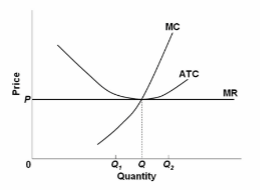
A. resources are overallocated to this product and productive efficiency is not realized.
B. resources are underallocated to this product and productive efficiency is not realized.
C. productive efficiency is achieved, but resources are underallocated to this product.
D. productive efficiency is achieved, but resources are overallocated to this product.
B. resources are underallocated to this product and productive efficiency is not realized.
You might also like to view...
At the midpoint of a linear demand curve, the price elasticity of demand is:
A) equal to zero. B) between zero and one. C) equal to one. D) greater than one.
An auction in which a seller begins by offering an item for sale at a relatively high price and then reduces the price by fixed amounts until receiving a bid is known as a:
A) Dutch auction. B) English auction. C) second-price auction. D) sealed-bid auction.
A Decrease in price will result in an increase in total revenue if:
a. the percentage change in quantity demanded is less than the percentage change in price. b. the percentage change in quantity demanded is greater than the percentage change in price. c. demand is inelastic. d. the consumer is operating along a linear demand curve at a point at which the price is very low and the quantity demanded is very high.
The real-balances effect on aggregate demand suggests that a:
A. Lower price level will decrease the demand for money, decrease interest rates, and increase consumption and investment spending B. Lower price level will decrease the real value of many financial assets and therefore cause an increase in spending C. Lower price level will increase the real value of many financial assets and therefore cause an increase in spending D. Higher price level will increase the real value of many financial assets and therefore cause an increase in spending