What is an optimal decision?
What will be an ideal response?
An optimal decision is one that best serves the objectives of the decision maker, whatever those objectives may be. It is selected by explicit or implicit comparison with the possible alternative choices. The term optimal connotes neither approval nor disapproval of the objective itself.
You might also like to view...
If you remove resources from factory production, the quantity of factory goods will
A) increase. B) decrease. C) be diverted to other production. D) remain the same but their price will decrease.
The period from the late 1990s to the winter of 2000 was marked by falling unemployment rates and falling inflation rates as well. How does economic theory explain this apparent violation of the Phillips curve model?
Suppose Country A and Country B are the only two countries in the world. Country A imports Good X from Country B and exports Good Y. In the absence of any transportation cost, at the world price of Good X
A. Country A's import demand curve will be perfectly inelastic. B. both Country A's import demand curve and Country B's export supply curve are positively sloped. C. Country A's import demand curve will intersect Country B's export supply curve. D. Country B's export supply curve is perfectly inelastic.
Refer to the table below for a certain product's market in Econland. If the world price of the product were $6 and a tariff of $1 per unit imported is imposed, then the quantity of output that would be supplied domestically would be:
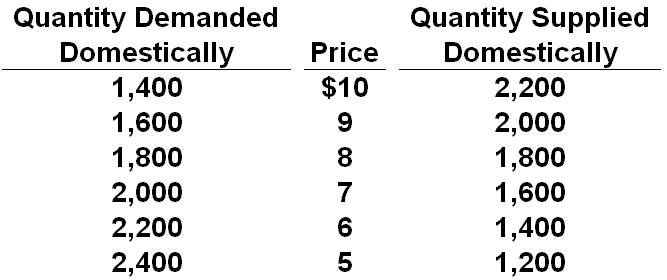
A. 1,400 units, and the quantity of output that would be imported would be 800 units
B. 1,600 units, and the quantity of output that would be imported would be 800 units
C. 1,600 units, and the quantity of output that would be imported would be 400 units
D. 1,400 units, and the quantity of output that would be imported would be 400 units