Figure 9-7 shows cost curves for Penny’s Parasols, a perfectly competitive firm. At which point(s) would Penny’s Parasols endure economic losses, but continue to produce in the short run?
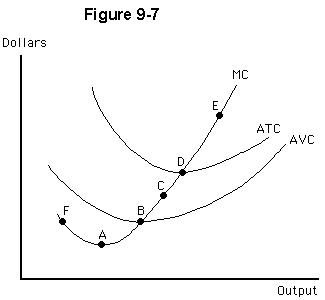
a.
D
b.
F
c.
A
d.
C
e.
E
d
You might also like to view...
Which of the following statements concerning the federal corporate income tax is true?
A) It is an efficient tax because it imposes a small excess burden relative to the tax revenue it raises. B) The corporate income tax is an example of the benefits-received principle. C) The incidence of the corporate income tax can be determined by using demand and supply analysis. D) Determining the incidence of the corporate income tax is complicated because it is not certain how corporations respond to the tax.
The most common measure of productivity shocks is known as
A) the Solow residual. B) the Lucas supply curve. C) the Prescott productivity parameter. D) the Kydland factor.
According to the New Classical macroeconomic school,
A) active policy intervention is ineffective. B) active policy intervention is undesirable and perverse. C) active policy intervention's benefits exceed its costs. D) active policy intervention's benefits are less than its costs.
Public goods are nonrival in ________ and their ________ are nonexcludable.
A. consumption; benefits B. production; benefits C. consumption; costs D. production; costs