The diagram concerns supply adjustments to an increase in demand (D 1 to D 2 ) in the immediate market period, the short run, and the long run. In the long run, the increase in demand will:
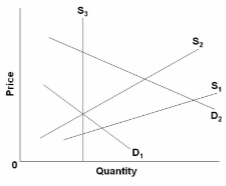
A. have no effect on either equilibrium price or quantity.
B. increase equilibrium price but not equilibrium quantity.
C. increase equilibrium quantity but not equilibrium price.
D. increase both equilibrium price and quantity.
D. increase both equilibrium price and quantity.
You might also like to view...
A compensating wage differential is
a. the difference between the wage of an individual working in favorable conditions and the wage of an individual working in unfavorable conditions b. compensation paid to an individual for working in a less desirable environment c. premium paid to a security holder to compensate him for bearing a higher risk d. Only A&B
If the price level increases, we would expect consumers to
A. raise their consumption functions. B. move downward along their consumption functions. C. lower their consumption functions. D. move upward along their consumption functions.
Mr. Smith is consuming beer and wine. At his current level of consumption, the marginal utility per dollar is 30 units for beer and 20 units for wine. Mr. Smith should
A. consume twice as much wine as beer. B. consume twice as much beer as wine. C. increase his consumption of beer relative to wine. D. increase his consumption of wine relative to beer.
The reason the substitution effect works to encourage a consumer to buy less of a product when its price increases is:
A. The real income of the consumer has been increased B. The real income of the consumer has been decreased C. The product is now relatively more expensive than it was before D. Other products are now relatively more expensive than they were before