Quotas are costly to consumers because
A. import competition increases for domestic goods.
B. the supply of the imported good increases.
C. consumers have to pay higher-prices.
D. the price of the imported good falls.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
In the graph shown above, if the government set a price ceiling of $26.
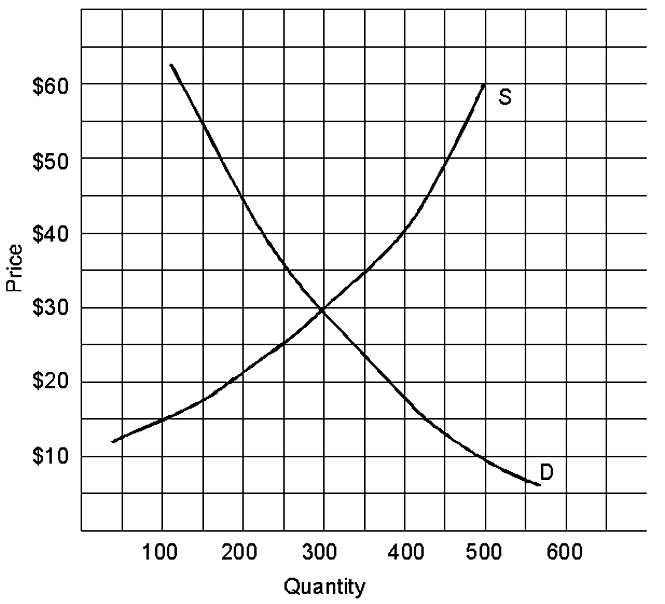
A. there would be a permanent shortage, at least until the price ceiling was lifted.
B. there would be a temporary shortage, then the price would fall to equilibrium price.
C. price would rise to the equilibrium price.
D. price would immediately fall to the equilibrium price.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 5.7 below to answer the question(s) that follow.
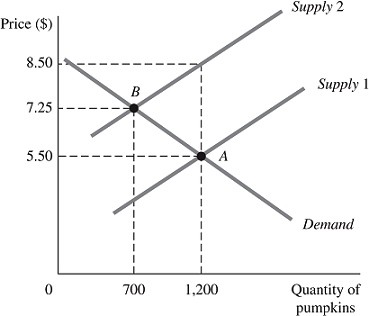 Figure 5.7The above figure represents the market for pumpkins both before and after the imposition of an excise tax, which is represented by the shift of the supply curve.Refer to Figure 5.7. Had the demand for pumpkins been perfectly inelastic at Point A, the price elasticity of demand for pumpkins from the equilibrium point before the imposition of the tax to the equilibrium point after the imposition of the tax would be
Figure 5.7The above figure represents the market for pumpkins both before and after the imposition of an excise tax, which is represented by the shift of the supply curve.Refer to Figure 5.7. Had the demand for pumpkins been perfectly inelastic at Point A, the price elasticity of demand for pumpkins from the equilibrium point before the imposition of the tax to the equilibrium point after the imposition of the tax would be
A. 1. B. 0. C. -1. D. infinity.
If a person is going to borrow $30,000 for a car and pay it off in monthly payments of $500 for 5 years, the internal rate of return is
A. 10%. B. 5%. C. 0%. D. 15%.
Suppose you are an economic researcher, and you have access to detailed information about all of the firms in a given geographic area. You would conclude that the pollution reduction policy in that area is efficient if you observe that:
A. all firms currently use the same pollution reduction technology. B. all firms produce approximately the same amount of pollution. C. the cleanest firms are also the most profitable. D. the marginal cost of reducing pollution is the same for all firms at current emissions levels.