Calculate Q, W, ?U, and ?H in each case. Take 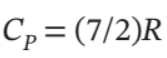 and
and 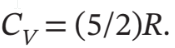
What will be an ideal response?
One mole of an ideal gas, initially at 30°C and 1 bar, is changed to 130°C and 10 bar by three different mechanically reversible processes:
? The gas is first heated at constant volume until its temperature is 130°C; then it is compressed isothermally until its pressure is 10 bar.
? The gas is first heated at constant pressure until its temperature is 130°C; then it is compressed isothermally to 10 bar.
? The gas is first compressed isothermally to 10 bar; then it is heated at constant pressure to 130°C.
Alternatively, take 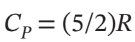 and
and 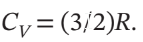
Of course, the overall ?U and ?H have to come out the same in every case, since the initial and final states are the same, but the total Q and W should, in general, be different for each case.
a. heating at constant volume followed by compression at constant temperature:
For the constant volume heating, W = 0, so Q = ?U = Cv?T = 5/2*R*(403 K – 303 K) = 2079 J/mol. As usual, ?H =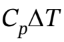 = 7/2*R*(403 K – 303 K) = 2910 J/mol. For the isothermal compression, ?U = ?H = 0, and Q = -W =
= 7/2*R*(403 K – 303 K) = 2910 J/mol. For the isothermal compression, ?U = ?H = 0, and Q = -W = 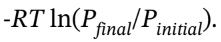 The initial pressure for this second step is 1 bar * (403 K/303 K) = 1.330 bar.
The initial pressure for this second step is 1 bar * (403 K/303 K) = 1.330 bar.
So, Q = -W = -R*303 K*ln(10/1.330) = -5082.438 J/mol. Adding the two steps gives, for the overall process, Q = 2079 J/mol – 5082.438 J/mol = -3003.438 J/mol, W = 5082.438 J/mol, ?U = 2079 J/mol, and ?H = 2910 J/mol.
You might also like to view...
The ____________________ is a detailed examination of the events that occurred in a test, exercise, or assessment function, from first detection to final recovery.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
?The Uniform Drawing System (UDS) modules are standards, guidelines, and other tools used to organize and present architectural information.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
What does tardiness imply to an interviewer?
a. Dependability b. Punctuality c. Conscientiousness d. No answers
Pneumatic controls operate by:
A) Hydraulic pressure. B) Air pressure. C) Electricity. D) Water pressure.