The economy pictured in the figure has a(n) ________ gap with a short-run equilibrium combination of inflation and output indicated by point ________. 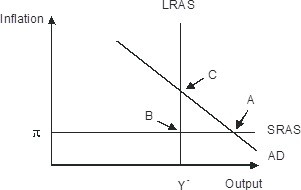
A. recessionary; A
B. recessionary; C
C. recessionary; B
D. expansionary; A
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
John Maynard Keynes and Friedrich Hayek
a. had similar views with regard to the cause of the Great Depression and what might be done to prevent it from happening again. b. both believed that perverse monetary policy was the primary cause of the ups and downs of the business cycle. c. both believed that budget deficits and surpluses could be used to smooth the ups and downs of the business cycle. d. had polar opposite views with regard to the underlying causes of economic booms and bust, but nonetheless their scholarly work commanded widespread respect among economists.
A rightward shift of a demand curve is called a(n):
A. increase in demand. B. decrease in demand. C. increase in quantity demanded. D. decrease in quantity demanded.
If the opportunity costs of producing a good increase as more of that good is produced, the economy's production possibility frontier will be
A. a negatively sloped straight line. B. negatively sloped and "bowed inward" toward the origin. C. negatively sloped and "bowed outward" from the origin. D. a positively sloped straight line.
Assume a perfectly competitive industry is in long-run equilibrium at a price of $150. If this industry is an increasing-cost industry and the demand for the product increases, long-run equilibrium will be reestablished at a price
A. of $150. B. greater than $150. C. less than $150. D. either greater than or less than $150 depending on the magnitude of the decrease in demand.