For a competitive firm, the marginal revenue product is:
A. always positive and nears zero as quantity increases.
B. always negative and nears zero as quantity increases.
C. decreasing eventually as quantity increases.
D. zero when profits are maximized.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Refer to the below graphs. (Assume that the pre-migration labor force in Country A is 0d and that it is 0u in country B.) The migration of labor from low-income country B to high-income country A will:
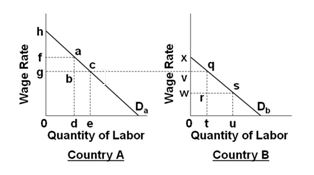
A. Increase wages in country A and decrease wages in country B
B. Decrease wages in country A and decrease wages in country B
C. Decrease wages in country A and increase wages in country B
D. Increase wages in country A and increase wages in country B
Refer to Table 11-1. Diminishing marginal returns sets in when the ________ worker is hired
A) 2nd B) 3rd C) 4th D) None of the above; the production function displays increasing marginal returns.
Potential advantages of nominal GDP targeting include
A) it implies that the central bank will respond to slowdowns in the real economy even if inflation is not falling. B) real GDP growth that is below potential or inflation that is below the inflation objective will encourage more expansionary monetary policy. C) it focuses not only on controlling inflation but also explicitly on stabilizing real GDP. D) all of the above.
Which of the following most accurately describes the aggregate supply curve?
a. It shows the price level associated with firms' unit costs and markups for any level of GDP. b. It is the sum of all individual firms' supply curves. c. It is determined by the federal government. d. It shows firms' unit costs for each level of GDP. e. It shows the equilibrium level of GDP corresponding to each price level.