How did an increase in consumer confidence change the final equilibrium point of the expansionary policy as shown in this graph?
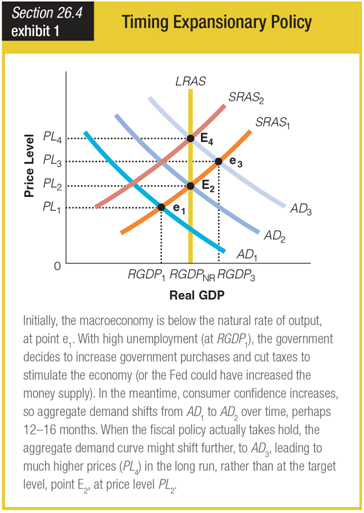
a. Instead of reaching the target of E3 and at RGDP3, the final result is E4 at RGDPNR.
b. Instead of reaching the target of E2 and at RGDPNR, the final result is E4 at RGDPNR.
c. Instead of reaching the target of E2 and at RGDPNR, the final result is E3 at RGDP3.
d. Instead of reaching the target of E3 and at RGDP3, the final result is E1 at RGDP1.
b. Instead of reaching the target of E2 and at RGDPNR, the final result is E4 at RGDPNR.
You might also like to view...
Cost-benefit analysis requires:
A) choosing the alternative with the least net benefit. B) all costs and benefits to be measured in the same unit. C) evaluating the budget constraint before making a choice. D) that the risks associated with different alternatives are ignored.
The growth rate of per capita real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is a reasonable measure of
A) the amount of money each person has. B) productive activity. C) personal well-being. D) quality of life.
The productivity of any input is independent and is not affected by the other resources that are used.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
1) The larger the number of firms and the less the degree of product differentiation, the greater will be the elasticity of a monopolistically competitive seller's demand curve. 2) The economic profits earned by monopolistically competitive sellers are zero in the long run. 3) The excess capacity problem associated with monopolistic competition implies that fewer firms could produce the same industry output at a lower total cost. 4) The demand curve of a monopolistically competitive firm is more elastic than that of a pure monopolist.