What are the effects of an increase in the population on potential GDP, the quantity of labor, the real wage rate, and potential GDP per hour of labor?
What will be an ideal response?
An increase in population increases the supply of labor. Employment increases and the real wage rate falls. The increase in employment creates a movement along the aggregate production function so potential GDP increases. Because of diminishing returns, potential GDP per hour of labor decreases.
You might also like to view...
Resources are all of the following EXCEPT
A) scarce and therefore require choices to be made. B) limited in quantity and can be used in different ways. C) unlimited and in abundance. D) the things we use to produce goods and services.
If an industry lacks barriers to entry and each of the many firm faces a demand curve with a negative slope, the industry is
A) perfectly competitive. B) monopolistically competitive. C) an oligopoly. D) a monopoly.
Assume the graph shown represents Grace's budget constraint. Which of the following is true?
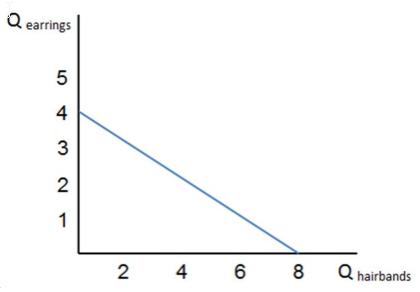
A. Grace's total utility is constant along her budget constraint.
B. Grace's marginal utility of each good is the same for each combination of goods on her budget line.
C. Grace's total expenditure is constant along her budget constraint.
D. Grace is indifferent between consuming any bundle that lies on the budget constraint.
Which of the following explains why the demand for money curve has an inverse relationship between the interest rates and the quantity of money demanded?
A. As the interest rate rises, the opportunity cost of holding money rises, and people respond by converting cash or checking account balances into interest-bearing financial investments. B. As the interest rate rises, people find it advantageous to borrow money, which increases the quantity of money demanded. C. As the interest rate falls, the opportunity cost of holding money rises, and people respond by converting cash or checking account balances into interest-bearing financial investments. D. As the interest rate rises, the demand for money curve shifts outward to the right.