A steel billet is to be heat treated by immersion in a molten salt bath. The billet is 5-cm-square and 1-m-long. Prior to immersion in the bath, the billet is at a uniform temperature of 20°C. The bath is at 600°C and the heat transfer coefficient at the billet surface is 20 W/(m2K). Plot the temperature at the center of the billet as a function of time. How much time is needed to heat the billet center to 500°C? Use an implicit difference scheme with node spacing of 1 cm. The thermal conductivity of the steel is 40 W/(m K) and the thermal diffusivity is 1 x 10–5 m2/s.
GIVEN
Steel billet undergoing heat treatment
FIND
(a) Temperature at the center of the billet as a function of time
(b) How much time is needed to heat the center of the billet to 500°C
The billet can be considered two-dimensional since it is very long. The accompanying sketch shows
the geometry.
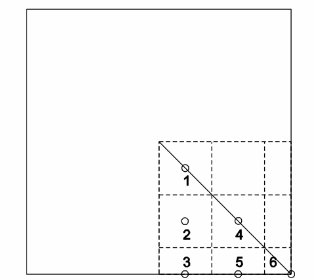
Allowing for symmetry, we need only consider 6 nodes and control volumes. These are also shown in
the sketch. We need to develop a heat balance on each of the these control volumes. In the implicit
form
Node (1)
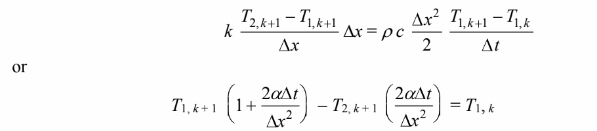
Node (2)
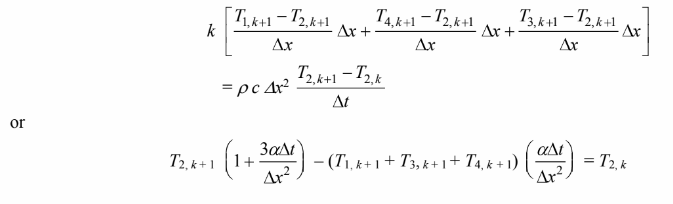
Node (3)
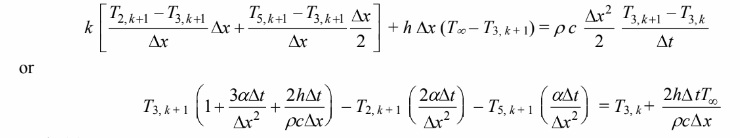
Node (4)
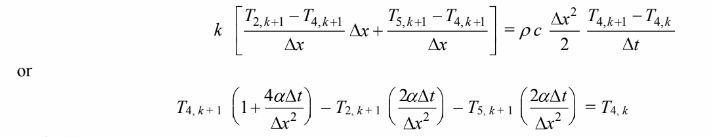
Node (5)
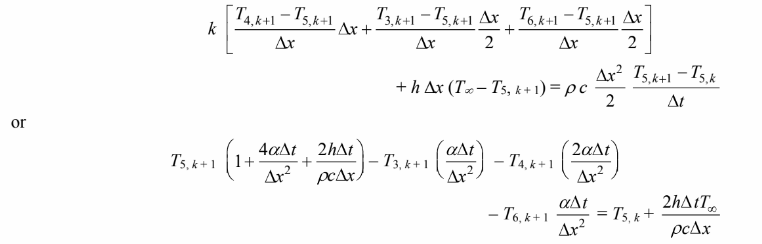
The 6 equations for the 6 control volumes can be written in matrix form as follows
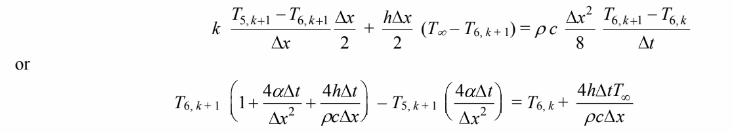
In the above matrix, we have used the following notation

The matrix equation can be written as
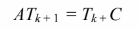
For k = 0, we know the vector Tk from the initial conditions. Therefore, we know the right-hand side of
the above equation. Inverting the matrix A and multiplying by both sides of the matrix equation, we
have the solution for Tk + 1
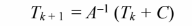
Incrementing k to k = 1, we can then insert the solution for T1 into the right-hand side of the above
equation to find T2 and so forth. This can be implemented fairly easily with a spreadsheet program in
two steps. First, the coefficients of the matrix A are determined from the problem parameters. The
matrix is then inverted. In the second step, the inverted matrix is repeatedly multiplied by the sum of
the two vectors Tk and C. Each time it is multiplied by the sum of these two vectors, the vector Tk is
updated with the results. The temperature at node 1 is nearest the center, so it is saved for later
plotting. The spreadsheet is shown below.


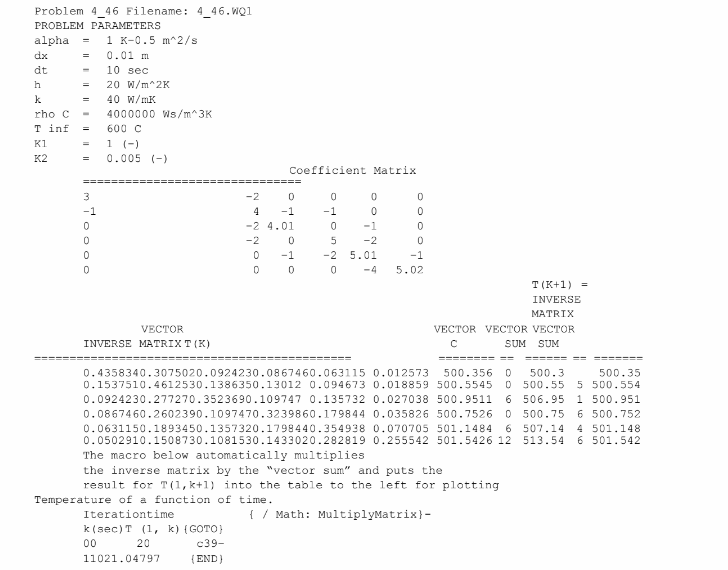
(b) The temperature at the billet centerline exceeds 500°C at 4440 seconds.
You might also like to view...
Estimate how many pennies you would have to stack to reach from the floor to an average 8-ft ceiling
A) 2 × 103 B) 2 × 102 C) 2 × 104 D) 2 × 105 E) 2 x 106
If we divide the mass of a star by its volume we calculate the star's ____________________
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
The allowed shapes for the orbits of objects responding only to the force of gravity are
A) ellipses, parabolas, and hyperbolas. B) ellipses only. C) ellipses, spirals, and parabolas. D) circles and ellipses.
How do we know that pulsars must be neutron stars?
A) Pulsars have the same upper mass limit as neutron stars do. B) No massive object, other than a neutron star, could spin as fast as we observe pulsars to spin and remain intact. C) This is only a theory that has not yet been confirmed by observations. D) We have observed massive-star supernovae produce pulsars. E) Telescopic images of pulsars and neutron stars look exactly the same.