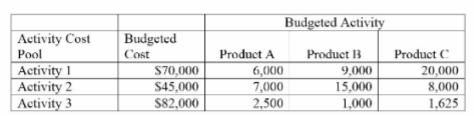
What are the activity rates for the three activities under activity-based costing?
A company uses activity-based costing to determine the costs of its three products: A, B,
and C. The budgeted cost and activity for each of the company's three activity cost pools are shown in the following table:
A) (1) $2.00; (2) $3.00; (3) $3.50.
B) (1) $3.50; (2) $1.50; (3) $32,80.
C) (1) $3.50; (2) $3.00; (3) $16.00.
D) (1) $2.00; (2) $1.50; (3) $16.00.
E) (1) $2.00; (2) $1.50; (3) $32.80.
D) (1) $2.00; (2) $1.50; (3) $16.00.
Explanation: (1) $70,000/(6,000 + 9,000 + 20,000) = $2.00
(2) $45,000/(7,000 + 15,000 + 8,000) = $1.50
(3) $82,000/(2,500 + 1,000 + 1,625) = $16.00
You might also like to view...
A correlation matrix indicates the coefficient of correlation between each pair of variables
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
An advantage of the single-step income statement over the multistep form is
A) the amount of information it provides. B) its simplicity. C) its comprehensiveness. D) its use in computing ratios.
List the prospect's five mental steps in buying.
What will be an ideal response?
Suppose a management accountant becomes aware of a confidential but illegal act that has occurred within her company. The management accountant must consider what she is ethically bound to do about this situation. Three alternative responses to this
situation are given below. State whether you agree or disagree with each, and briefly detail your reasons. a. The accountant must remain loyal to the company at all times and should report the occurrence only to appropriate officials within the company. b. The accountant is bound to inform officials only if she stands to personally gain (make money) from knowledge of the illegal act. c. The accountant must exercise personal judgment; a clear-cut answer does not exist given the limited information provided.