Profit-maximizing level of output
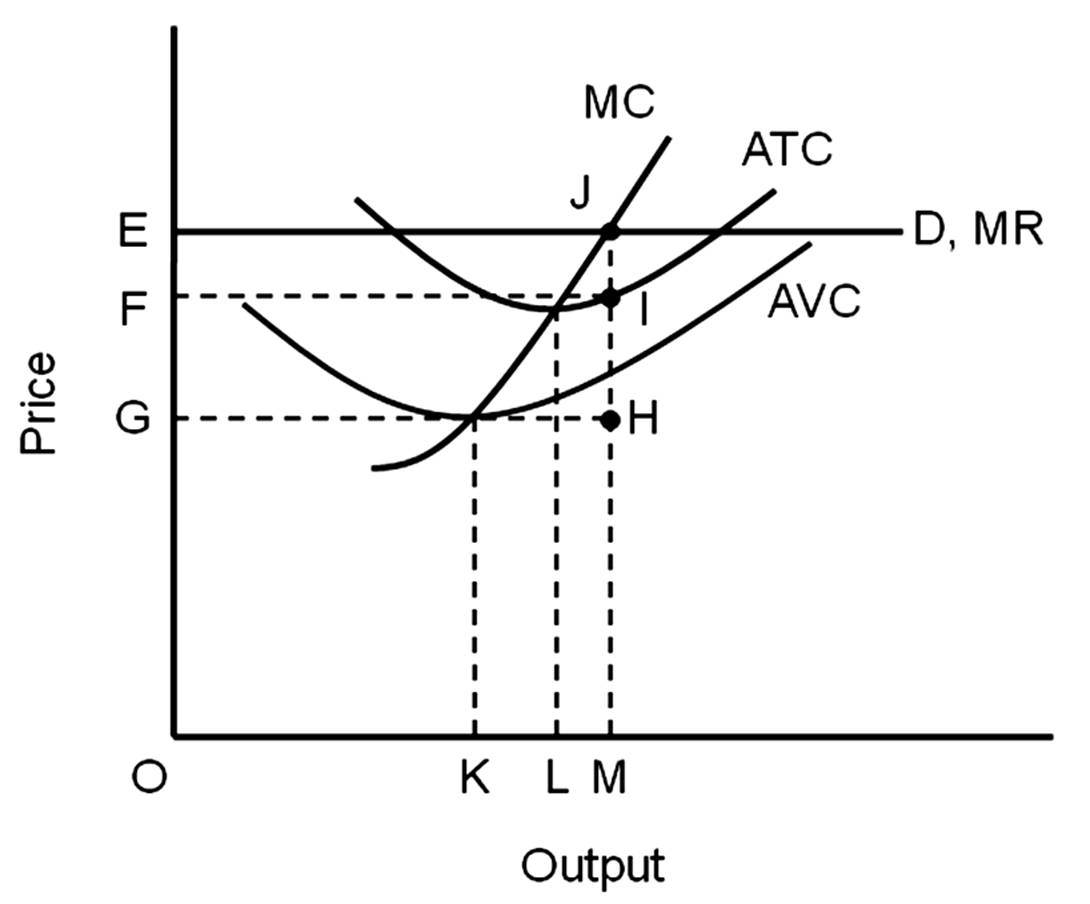
A. is OK.
B. is OL.
C. is OM.
D. cannot be found on this graph.
C. is OM.
You might also like to view...
Developing countries are usually unwilling to negotiate over labor standards because
A) the WTO always tends to rule in favor of industrialized nations. B) they fear that industrialized nations are trying to undermine their comparative advantage—production of agriculture and textiles/apparel—and close the markets of high-income countries in these areas. C) they fear that they may be unable to compete without some protection of their industries. D) they don't have a comparative advantage in any good at all. E) organized labor would not allow them to negotiate with other countries.
The American Tire Company has been experiencing a steady loss of market over the past 40 years due to imports of lower-priced tires. Which argument would American Tire most likely present to Congress when it lobbies for trade restrictions?
a. infant industry argument b. declining industry argument c. national defense argument d. antidumping argument e. loss of domestic jobs
Assume that several firms compete in the market for cellular phones and that the price elasticity for this industry is equal to 0.75. Based on this information, would you advise a firm in this industry to increase its price? If so, what is the percentage loss in total sales this firm should expect to experience?
A. Definitely no. Each 1 percent increase in price would result in 7.5 percent reduction in total sales, negatively affecting total revenues. B. Definitely yes. Total revenues would increase as sales would decrease by only .75 percent for each 1 percent increase in price. C. Not enough information is provided to make a sound decision. For the same reason, it is not possible to predict what the loss in sales for one firm would be. D. Definitely no. Each 1 percent increase in price would result in 7.5 percent reduction in total sales, affecting total revenues positively.
Suppose an event occurs that causes people to lose faith in the ability of Europeans to pay their euro-denominated debt. Suppose that before this happens the exchange rate between the euro and the dollar is .75 euros/dollar. The resulting exchange rate would likely
A. cause the exchange rate to have to be expressed in dollars per euro (because the other way would no longer make sense). B. rise to (perhaps) .9 euros/dollar. C. fall to (perhaps) .6 euros/dollar. D. remain unchanged.