When the output of an economy exceeds the economy's full-employment capacity,
a. aggregate supply will increase until the economy can produce the output at the existing price level.
b. the actual rate of unemployment will be less than the natural rate.
c. wage rates and resource prices will tend to fall.
d. interest rates will decline and help direct the economy back to full employment.
B
You might also like to view...
In the early twentieth century, general stores in the upper Midwest had more power over prices because:
a. they acted as intermediaries between farmers and buyers. b. the transportation network was bad, leaving farmers and buyers with no alternatives except the general stores in small towns. c. inventories at the general stores were low and demand was high. d. stockouts were a chronic problem and there was little variety.
Refer to the accompanying figure. Suppose the solid line shows the current demand for coffee. In response to news that next year's coffee harvest will be extremely good due to favorable weather conditions, you should expect: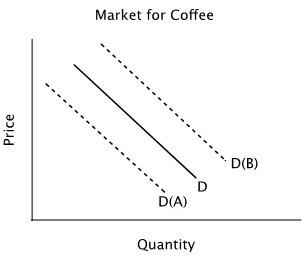
A. the demand curve to shift to D(B) in anticipation of lower future prices. B. the quantity of coffee demanded to decrease, but no shift in the demand curve. C. the demand curve to shift to D(A) in anticipation of lower future prices. D. neither a change in quantity demanded nor a shift in demand because it will be a long time before next year's coffee crop is harvested.
Refer to the diagram. The direct economic impact of the destruction and loss of lives caused by the terrorist attacks of September 11, 2001, is illustrated by the:
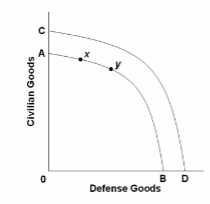
A. shift of the production possibilities curve from CD to AB.
B. shift of the production possibilities curve from AB to CD.
C. move from x to y on production possibilities curve AB.
D. move from y to x on production possibilities curve AB.
Between 1953 and 2007, rising labor productivity contributed more to U.S. economic growth than did increases in inputs.
a. true b. false