Refer to the information provided in Table 14.3 below to answer the question that follows.
Table 14.3B's Strategy
?AdvertiseDon't Advertise??A's profit $75 millionA's profit $200 million?AdvertiseB's profit $75 millionB's profit $50 millionA's Strategy????Don'tA's profit $50 millionA's profit $100 million?AdvertiseB's profit $200 millionB's profit $100 millionRefer to Table 14.3. The result of this game is known as a
A. repeated strategy.
B. tit-for-tat outcome.
C. collusive outcome.
D. prisoners' dilemma.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
What sort of productivity shocks would cause lower real wage growth and result in lower growth in labor productivity?
A) productivity shocks which decrease supply of labor given the demand for labor B) productivity shocks which increase supply of labor given the demand for labor C) productivity shocks which increase demand for labor given the supply of labor D) productivity shocks which decrease demand for labor given the supply of labor
Suppose the current account of a country is initially in balance. A new transaction occurs so that the current account is now in surplus. Official reserve balance is maintained before and after the transaction occurs. From this, we know that
A) the balance of trade is now in surplus. B) the balance of goods and services is now in surplus. C) the capital account is now in deficit. D) the government must make official reserve transactions.
The desire to have a relatively even pattern of consumption over time is known as
A. excess sensitivity. B. the consumption-smoothing motive. C. the substitution effect. D. forced saving.
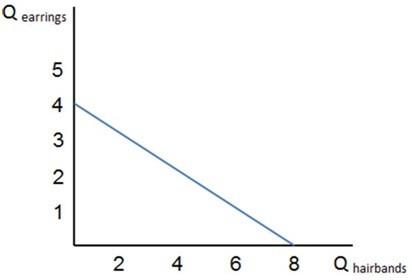 If the graph shown represents Celia's budget constraint, which of the following must be true?
If the graph shown represents Celia's budget constraint, which of the following must be true?
A. Celia gets twice as much utility from earrings as she does from hairbands. B. Celia will spend twice as much on earrings as she does hairbands. C. Celia could consume either four pairs of earrings or eight hairbands. D. All of these are true.