Maggie is trying to convince her friend Hannah to spend the morning at the beach instead of studying economics. Maggie’s argument is that the beach is free so will not cost Hannah anything to go. Maggie even volunteers to drive. Maggie’s argument
a. is correct; it is free to go to the beach.
b. is forgetting Hannah’s opportunity cost of not being able to study.
c. assumes Hannah has to eat at home or the beach so it will not cost Hannah additional money.
d. is forgetting sunk costs.
b. is forgetting Hannah’s opportunity cost of not being able to study.
You might also like to view...
A science that studies the behavior and interactions of human beings, individually and in groups, is known as a(n)
a. social science. b. physical science. c. interactive science. d. dynamic science.
The aggregate demand curve:
a. would be little affected by a technological advancement. b. shifts to the right when spending decreases. c. shifts to the left when there is a decrease in taxes. d. cannot move independently of the aggregate supply curve. e. shifts to the right when there is an expectation that future income will fall.
Using Figure 1 below, if the aggregate demand curve shifts from AD1 to AD2 the result in the long run would be:
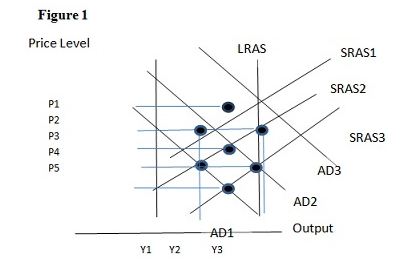
A. P1 and Y2.
B. P3 and Y1.
C. P2 and Y3.
D. P2 and Y2.
Clorox Bleach and generic brands have the exact same proportions of chlorine and other active ingredients. The reason that people continue to purchase Clorox at twice the price of the generic brand is the
a. price elasticity of demand classifies them as belonging to the same market b. low cross elasticity between Clorox and the generic brand c. high cross elasticity between Clorox and the generic brand d. perceived differences on the part of consumers e. income elasticity of demand is higher for the Clorox brand