Which of the following events would cause the price of oranges to fall?
a. There is a shortage of oranges.
b. The FDA announces that bananas cause strokes, and oranges and bananas are substitutes.
c. The price of land throughout Florida decreases, and Florida produces a significant proportion of the nation's oranges.
d. All of the above are correct.
c
You might also like to view...
Regarding economic models, which of the following statements is NOT true?
A. An economic model is a simplified representation of a theory or part of a theory. B. An economic model can provide clear answers for policy makers. C. An economic model can clarify an important economic problem. D. An economic model can show three-variable diagrams.
Three firms agree to operate as a monopoly and charge the monopoly price of $40 for their product and (jointly) produce the monopoly quantity of 50,000 units. If the competitive price for the product is $35, under the Clayton Act these three firms face treble damages of ________.
A) $1,000,000 B) $250,000 C) $3,000,000 D) $750,0
Figure 2-8
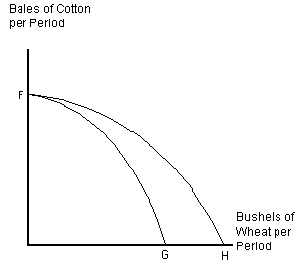
Assume that U.S. agricultural land is used either to raise cotton for clothing or to grow wheat. Curve FG in represents the current production possibilities frontier for cotton and wheat. What could cause the production possibilities frontier to shift from FG to FH?
a.
a change in government subsidies that favors wheat production over cotton production
b.
development of a new fertilizer that improves production of wheat, but has no impact on cotton production
c.
development of a new fertilizer that improves production of cotton, but has no impact on wheat production
d.
newly reclaimed swampland that is equally suited to growing either crop
e.
newly reclaimed swampland that can be used to grow either crop, but is better suited to growing wheat
An auxiliary regression refers to a regression that is used:
A. when the dependent variables are qualitative in nature. B. when the independent variables are qualitative in nature. C. to compute a test statistic but whose coefficients are not of direct interest. D. to compute coefficients which are of direct interest in the analysis.