At what point is a packet considered to be a giant?
a. It becomes a giant when it exceeds the medium's maximum packet size.
b. It becomes a giant when it exceeds 1500 bytes.
c. It becomes a giant only when fragmented pieces are reassembled and the packet size is too large.
d. It becomes a giant once a VLAN tag is added.
ANSWER: a
You might also like to view...
A private attribute on a class diagram:
A) does not change its value for different object instances. B) is hidden from all classes except immediate subclasses. C) is only available in the object. D) is available to the class and all classes that have relationships with the attribute's class.
Rewrite the following conditional expressions without any NOT operators so that the logical outcome is unchanged for all values of the variable x. Then evaluate the original expression and the equivalent expression using the values: x = 1, y = 1, z = 1. Compare the results.
Notes: The NOT operator applies to the part of the expression enclosed in parentheses that follows immediately. Evaluating the original and equivalent expressions for the values given is only a partial check. A general check can be done with a truth table. NOT (x = 1) AND NOT (x = 2) (x<>1)AND(x<>2)
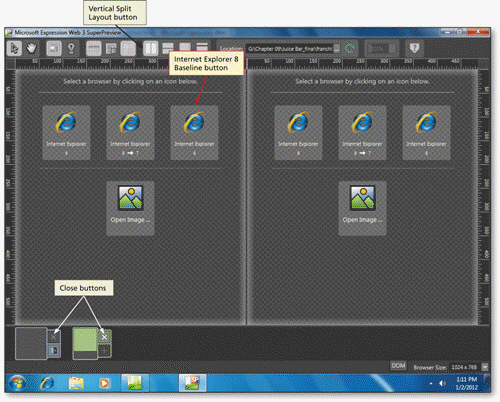 Explain the feature shown in the accompanying figure, and what it is used for.
Explain the feature shown in the accompanying figure, and what it is used for.
What will be an ideal response?
You can rename a slide master by clicking Rename in the ____ group.
A. Edit Master B. Slide Master C. View Master D. Master Views