The ____________ defenses of the body protect against many different types of pathogens. For this reason, they are also referred to as the ____________ defenses.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
Answer: Innate; Nonspecific
You might also like to view...
Choose the evidence supporting the argument that a small number of changes in developmental regulatory genes can result in large phenotypic changes.(choose all that apply)
_____ Closely related animals can have very different patterns of development. _____ Most developmental genes are highly conserved. _____ Much of phenotypic variation is environmentally caused. _____ The developmental "toolkit" consists of a large number of genes. Clarify Question · What is the key concept addressed by the question? · What type of thinking is required? · What key words does the question contain and what do they mean? Gather Content · What do you already know about developmental regulatory genes? Consider Possibilities · Consider the different answer options. Which can you rule out? Choose Answer · Given what you now know, what information and/or problem solving approach is most likely to produce the correct answer? Reflect on Process · Did your problem-solving process lead you to the correct answer? If not, where did the process break down or lead you astray? How can you revise your approach to produce a more desirable result?
Answer the following statements true (T) or false (F)
1. Bacterial cells always contain one copy of a circular chromosome. 2. Bacteria can exchange DNA between strains of the same species and between different species. 3. Viroids have a genome but do not translate any of it to protein. 4. All forms of horizontal gene transfer require both the recipient and donor bacteria to be alive.
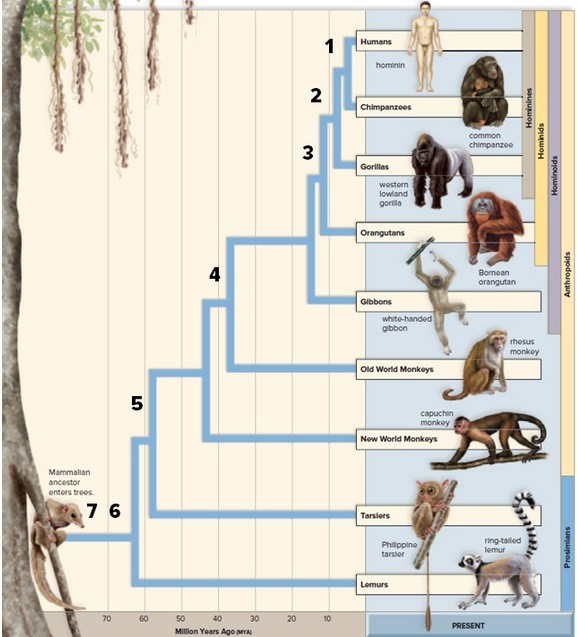 Where on this phylogenetic tree of primate evolution do you find the evolution of humans and species very closely related to humans?
Where on this phylogenetic tree of primate evolution do you find the evolution of humans and species very closely related to humans?
A. No. 1 B. No. 2 C. No. 3 D. No. 4 E. No. 5
The secondary antibody response is ________ because of antigen stimulation of ________
a. high titer / T cells b. low titer / memory cells c. rapid / memory cells d. mostly IgM / B cells