What is critical for developing a causal analysis but can be an insurmountable problem with a cross-sectional design?
A. time order
B. association
C. nonspuriousness
D. mechanism
A. time order
You might also like to view...
Campaign blogs and podcasts
A. have improved candidates' ability to deliver their message to voters without media filter. B. have made it more difficult for candidates to control their campaigns. C. are not followed by mainstream news media. D. are sometimes created for the candidate by professional strategists. E. have improved candidates' ability to deliver their message to voters without media filter, and are sometimes created for the candidate by professional strategists.
An indirect form of democracy in which the people choose leaders to fill government posts is called ________ democracy
A) popular B) representative C) pure D) direct E) republican
Among the incentives to join noneconomic interest groups are all except which of the following?
a. Passion for the goals of the group b. Chance to be elected to office c. Social pressure from peers d. Selective incentives e. Threat of ostracism from the life of the community
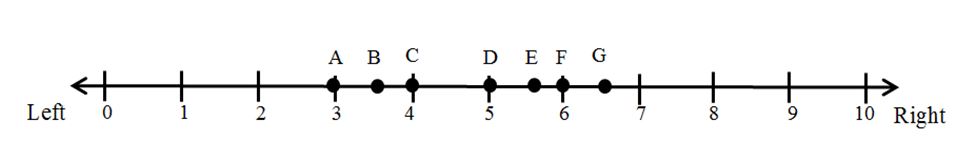
Let’s suppose that P1 locates at Position 2 on the left–right issue dimension and that P2 locates at Position 7. Who wins the election in the situation illustrated by Figure 1?
Figure 1 illustrates an election in which there are seven voters (A, B, C, D, E, F, G) arrayed along a single left–right issue dimension that runs from 0 (most left) to 10 (most right).Each voter is assumed to have a single-peaked preference ordering over the issue dimension and to vote for the party that is located closest to her ideal point.The voters are participating in a majority rule election in which there are two parties, P1 and P2, competing for office.These parties can be thought of as “office-seeking” parties since they only care about winning the election and getting into office.
A. The two parties tie.
B. P1 wins.
C. P2 wins.