A third-quarter Moon is visible
a. near the eastern horizon just before sunrise.
b. near the eastern horizon just after sunset.
c. in the southern sky at sunrise.
d. in the southern sky at sunset.
e. from sunset until sunrise.
c
You might also like to view...
A transverse periodic wave is represented by the equation y(z, t) = -2.0 cm sin(1,200 rad/s t - 20.0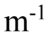 x). Another transverse wave is represented by the equation y(z, t) = +2.0 cm sin(1,200 rad/s t + 20.0
x). Another transverse wave is represented by the equation y(z, t) = +2.0 cm sin(1,200 rad/s t + 20.0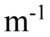 z). What is the equation that represents the superposition of the two waves?
z). What is the equation that represents the superposition of the two waves?
A. y(z, t) = 4.0 cm sin(1,200 rad/s t - 20.0 z)
z)
B. y(x, t) = 4.0 cm sin(1,200 rad/s t)cos (20.0 x)
x)
C. y(x, t) = +4.0 cm cos(1,200 rad/s)sin (20.0 x)
x)
D. y(x, t) = +4.0 cm cos(1,200 rad/s) + (20.0 x)
x)
Where do we find our star on the H-R diagram?
A) In the middle of the main sequence B) On the far left of the main sequence C) With the red giants D) On the lower left
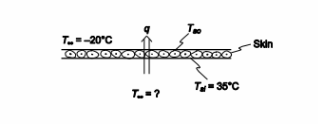
In order to prevent frostbite to skiers on chair lifts, the weather report at most ski areas gives both an air temperature and the wind chill temperature. The air temperature is measured with a thermometer that is not affected by the wind. However, the rate of heat loss from the skier increases with wind velocity, and the wind-chill temperature is the temperature that would result in the same rate of heat loss in still air as occurs at the measured air temperature with the existing wind. Suppose that the inner temperature of a 3-mm-thick layer of skin with a thermal conductivity of 0.35 W/(m K) is 35°C and the ambient air temperature is –20°C. Under calm ambient conditions the heat transfer coefficient at the outer skin surface is about 20 W/(m2 K) but in a 40 mph wind it increases to
75 W/(m2 K). (a) If frostbite can occur when the skin temperature drops to about 10°C, would you advise the skier to wear a face mask? (b) What is the skin temperature drop due to wind?
GIVEN
• Skier’s skin exposed to cold air
• Skin thickness (L) = 3 mm = 0.003 m
• Inner surface temperature of skin (Tsi) = 35°C
• Thermal conductivity of skin (k) = 0.35 W/(m K)
• Ambient air temperature (T?) = –20°C
• Convective heat transfer coefficients
? Still air (hc0) = 20 W/(m2 K)
? 40 mph air (hc40) = 75 W/(m2 K)
• Frostbite occurs at an outer skin surface temperature (Tso) = 10°C FIND
(a) Will frostbite occur under still or 40 mph wind conditions? (b) Skin temperature drop due to wind chill.
ASSUMPTIONS
• Steady state conditions prevail
• One dimensional conduction occurs through the skin
• Radiative loss (or gain from sunshine) is negligible
SKETCH
A block is launched up an incline plane. After going up the plane, it slides back down to its starting position. The coefficient of friction between the block and the plane is 0.3 . The speed of the block when it reaches the starting position on the trip down:
a. is the same as the launching speed. b. is less than the launching speed. c. is more than the launching speed. d. cannot be compared to the launch speed with the information given.