The owners of Market Analysts, a business and economics consulting firm, are big believers in paying benchmark competitive wages. They pay all (nonlegally specified) compensation in wages. If an employee wants a benefit, the company has an insurance program, but it comes out of the employee's paycheck. Market Analysts tends to hire very young workers just out of college. They are energetic and work hard, but after two years they tend to leave for other firms, taking valuable training with them. If Market Analysts wants to keep its employees, what changes should it make to the terms of employment offered to new employees?
What will be an ideal response?
The problem is that the overall level of compensation (salary and fringe benefits) is high enough to attract recent college graduates, but the compensation package is not great enough to retain experienced workers. The firm has to offer a more competitive package of monetary compensation and fringe benefits in order to retain its employees. Young college graduates may have different preferences for fringe benefits than slightly more experienced employees who are starting families. This firm's human resource compensation packages are quite competitive for entry-level workers, but do not provide more experienced workers enough fringe benefits to keep them around. This firm should discover what benefits employees want in order to remain on the job. On the graph below, any compensation offer of salary, which is measured on the vertical axis, does not meet the displayed reservation level of utility for the experienced worker. An offer of (S*, F*) would be the cost-minimizing way to keep these valuable employees.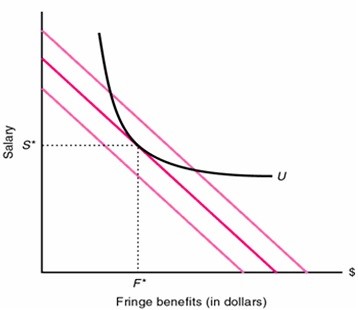
You might also like to view...
Gains from trade
A) result in being able to consume beyond the trading individuals' production possibilities frontiers. B) occur when one party to the trade has an absolute advantage in both goods. C) occur when people do not specialize. D) occur when opportunity costs are equal. E) always benefit one party but not the other party of any trade.
Keeping in mind the Coase theorem, in the figure above, if the residents of the town own the lake, the market does what?
A) overproduces 120 tons of pesticide B) underproduces 120 tons of pesticide C) overproduces 60 tons of pesticide D) produces the efficient quantity of pesticide
For dessert, Mac has the choice between cheesecake and apple pie. The cheesecake has a marginal utility of 50 and a price of $5, and the apple pie has a marginal utility of 30 and a price of $3 . Therefore, Mac should buy
a. the cheesecake since the marginal utility is greater b. the apple pie because its price is lower c. two servings of apple pie and no cheesecake d. four servings of cheesecake e. either the apple pie or the cheesecake, it makes no difference
The equation of exchange shows that the total spending in an economy is always greater than the total receipts
Indicate whether the statement is true or false