To predict the effects of a tax cut on consumption spending, economists must have some estimate of the
a. income effect.
b. substitution effect.
c. relative price effect.
d. marginal propensity to consume.
d
You might also like to view...
If individuals who sit in the back of the classroom receive lower grades on average than the rest of the class, does that mean that sitting in the back of a classroom causes one to perform poorly on exams? a. Not necessarily. The reoccurrence of a certain relationship between two variables does not necessarily imply causation. b. It is not possible for an economist to determine causation
between variables. c. The reoccurrence of such a relationship is sufficient evidence that sitting in the back of a classroom will lead to lower grades. d. none of the above
Jennifer buys a piece of costume jewelry for $33 for which she was willing to pay $42. The minimum acceptable price to the seller, Nathan, was $30. Jennifer experiences:
A. a consumer surplus of $12 and Nathan experiences a producer surplus of $3. B. a producer surplus of $9 and Nathan experiences a consumer surplus of $3. C. a consumer surplus of $9 and Nathan experiences a producer surplus of $3. D. a producer surplus of $9 and Nathan experiences a producer surplus of $12.
Refer to the figure below. In response to gradually falling inflation, this economy will eventually move from its short-run equilibrium to its long-run equilibrium. Graphically, this would be seen as 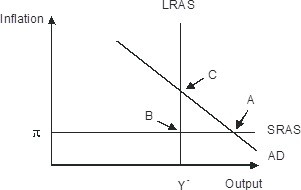
A. long-run aggregate supply shifting leftward B. Short-run aggregate supply shifting upward C. Short-run aggregate supply shifting downward D. Aggregate demand shifting leftward
Which of the following statements is correct?
A. Marginal utility is the cumulation or summation of total utility B. Total utility is the cumulation or summation of marginal utility C. Total utility is the product of multiplying price times marginal utility D. Total utility is the change in marginal utility as quantity consumed increases