List the steps on how to use the DRL.
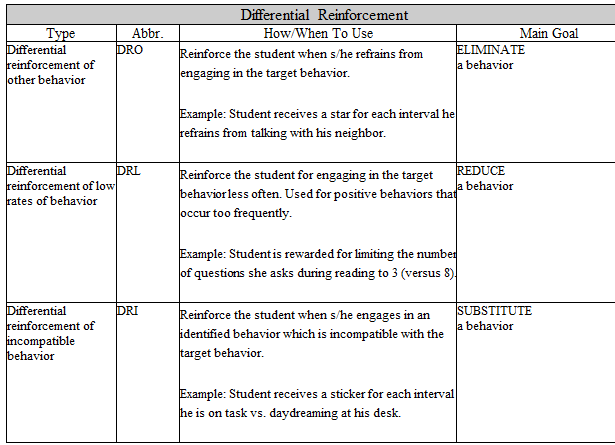
1. Identify the behavior to be decreased.
2. Determine the rate (e.g., frequency, duration) of the behavior (collect baseline data).
3. Identify the desired rate for the behavior to occur.
4. Determine the first behavioral goal at which reinforcement for lowered frequency will occur. Continue to decrease this behavioral goal throughout the DRL procedure.
5. Reinforce the student for meeting the behavioral goal.
6. Continue to set expectations for lower rates of behavior, reinforcing the student for meeting each subsequent level.
You might also like to view...
A teacher hangs up three paintings by famous artists. Her first-graders gather around the one with the most colors and ignore the other two. Based on this, she decides that her students:
a. are attracted to colors, like most young children. b. have very unique preferences for art. c. don't know much about the arts. d. need to look at more paintings.
Choose the statement that is not a typical sign of AD/HD?
a. Difficulty in focusing attention in play activities or other tasks b. Difficulty in listening when spoken to c. Apparent inability to follow through on instructions d. Ease in transitioning from one activity to another
Which of the following statements about learning disabilities is true?
A. Learning disabilities are usually recognized and diagnosed during the toddler or preschool years. B. We must eliminate other possible causes of the child's difficulty in school (such as vision loss or mental impairment) before we make a diagnosis of learning disabilities. C. About 10% of the children in special education classrooms have been diagnosed as learning disabled. D. Children with learning disabilities are often very popular among their peers because of their friendliness.
Answer the following statement(s) true (T) or false (F)
When we compute many correlations in a single study, we report each correlation coefficient in a table called a correlation matrix.