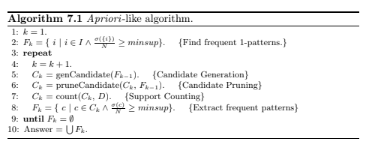
Many association analysis algorithms rely on an Apriori-like approach for finding frequent patterns. The overall structure of the algorithm is given below.
Suppose we are interested in finding boolean logical rules such as
{a ? b} ?? {c, d},
which may contain both disjunctions and conjunctions of items. The corre-
sponding itemset can be written as {(a ? b), c, d}.
(a) Does the Apriori principle still hold for such itemsets?
(b) How should the candidate generation step be modified to find such
patterns?
(c) How should the candidate pruning step be modified to find such pat-
terns?
(d) How should the support counting step be modified to find such pat-
terns?
Refer to R. Srikant, Q. Vu, R. Agrawal: Mining Association Rules
with Item Constraints. In Proc of the Third Int’l Conf on Knowledge
Discovery and Data Mining, 1997.
You might also like to view...
Two tasks that are operating ________ are both making progress at once.
a. sequentially b. concurrently c. iteratively d. recursively
Critical Thinking QuestionsCase 3-1 The second image is a digital photograph and a color cast has occurred. How can you improve the photograph's color? a. change the color saturationc. apply recolor effectsb. change the color toned. reshoot the picture
What will be an ideal response?
Clicking a menu name on the menu bar opens a dialog box.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
The purpose of the DummyContent.java file is to provide sample code you customize to suit your specific app content.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)