A monopoly produces widgets at a marginal cost of $20 per unit and zero fixed costs. It faces an inverse demand function given by P = -100 ? 4Q. Suppose fixed costs rise to $401. What happens in the market?
A. The firm will reduce its output and raise price.
B. The firm will raise the price.
C. The firm will continue to produce the same output and charge the same price.
D. The firm will shut down immediately.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
The equilibrium price for a British pound is $1.60. At a price of $1.75 per British pound, there would be excess __________ the dollar and the dollar would __________
A) supply of; appreciate B) supply of; depreciate C) demand for; appreciate D) demand for; depreciate
Bid-rigging has all of these features EXCEPT
a. It is a collusive agreement b. The bid-riggers pay a smaller amount than without bid-rigging c. Bid-riggers need an auxiliary mechanism to allocate the good within the bid-riggers d. Bid rigging is usually a legitimate and legal strategy for the buyer-side
If the government set a price floor at $18
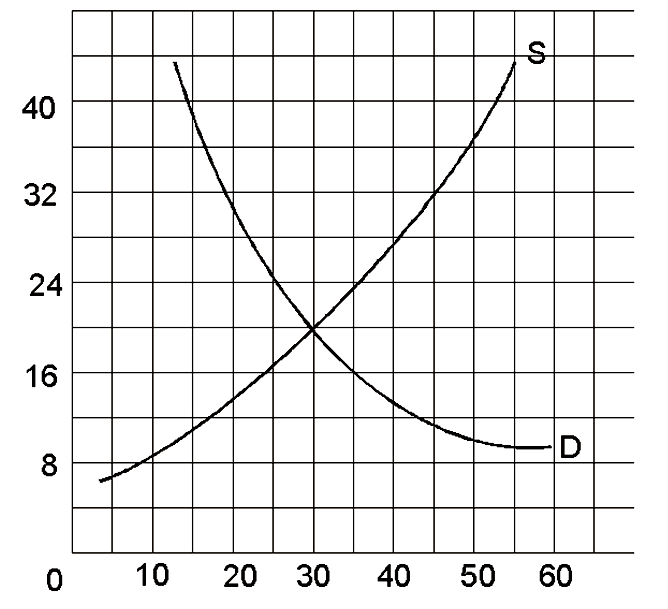
A. there would be a temporary surplus, then prices would fall to equilibrium.
B. the price floor would not have any effect on this market.
C. then quantity demanded would be greater than quantity supplied.
D. there would be a permanent surplus, at least until the price floor was lifted.
The Coase theorem states that if private parties can negotiate the purchase and sale of the right to perform activities that cause externalities, then they:
A. will never arrive at efficient solutions to the problems caused by externalities. B. will never perform activities that generate negative externalities. C. will always perform activities that generate positive externalities. D. can always arrive at efficient solutions to the problems caused by externalities.